What is blanking in sheet metal? It’s a process where specific shapes are cut from metal sheets, creating precise pieces used for further fabrication or assembly.
As a CNC Machinist, I often get asked about blanking and how it helps create uniform parts with high precision for various projects.
Don’t worry, the process is simple and widely used in manufacturing.
In this guide, you will learn how blanking works, the tools involved, and why it’s an important step in producing metal parts efficiently.
Let’s jump right in!
1. Defining Blanking in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Blanking in sheet metal fabrication is a precision cutting technique where a piece is removed from a larger metal sheet, employing a meticulously crafted die and punch. This method is vital for creating parts with exact dimensions and shapes, making it ideal for high-volume, consistent production. Its versatility allows for the processing of various metals, catering to a broad range of industrial requirements.
The distinct advantage of blanking lies in its ability to produce components with clean, burr-free edges, essential for high-quality finishes. This process is not only efficient but also capable of handling complex designs, which is crucial in sectors demanding precision. Blanking stands out for its balance of accuracy and productivity, making it a fundamental process in the manufacturing of diverse metal parts.
2. Types of Blanking Operations
Building on the fundamental understanding of blanking in sheet metal fabrication, let’s explore its various types, each tailored to meet specific manufacturing requirements. Here are some of its types:
Punch Press Blanking
Punch press blanking is a common and efficient method, utilizing a die and a punch to shape metal sheets. It’s characterized by its high speed and suitability for large-volume production, making it a popular choice in industries requiring mass production of uniform parts. This method is especially effective for simpler shapes and standard thickness materials.
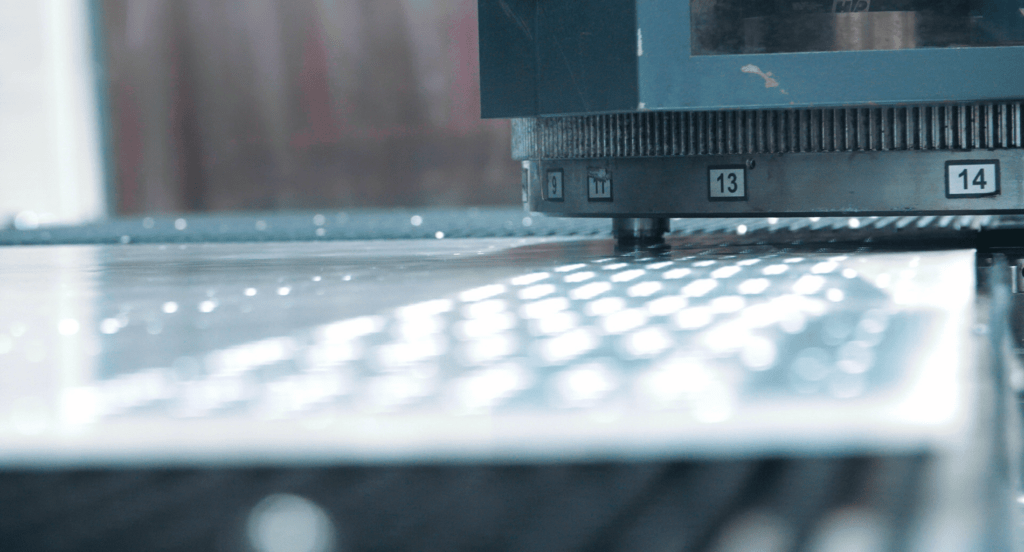
Fine Blanking
Fine blanking known for its ability to produce parts with very smooth edges and high dimensional accuracy, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.12% from 2022 to 2028, according to Market Research. This precision-focused technique is often used for components that require tight tolerances, such as those found in automotive and precision engineering industries. The process ensures minimal post-processing, saving time and resources.
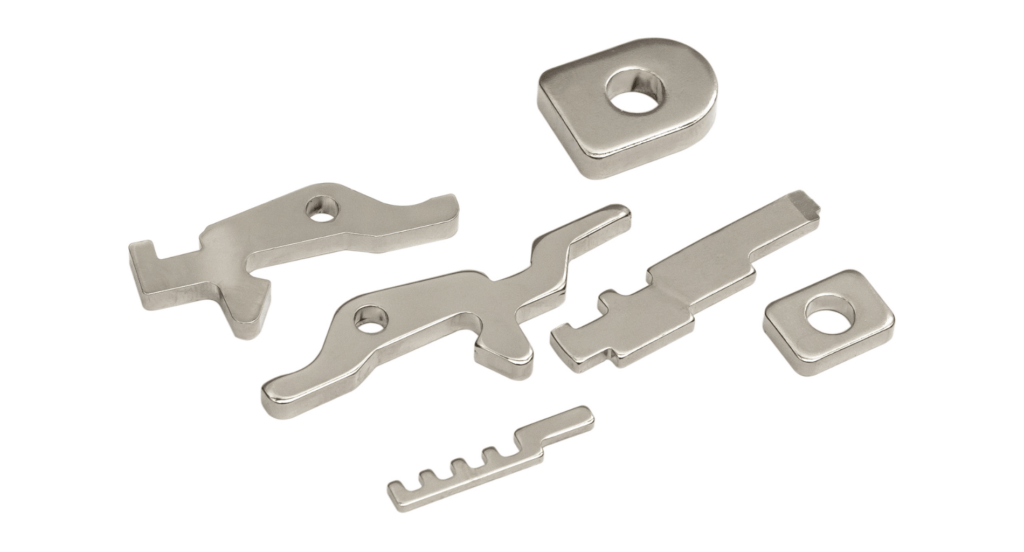
Progressive Die Blanking
Progressive die blanking is a consecutive process that combines forming and cutting operations into one continuous operation. It’s ideal for manufacturing complex parts, as it reduces the need for multiple setups and handling, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. This method is particularly advantageous for detailed designs and high-volume production.
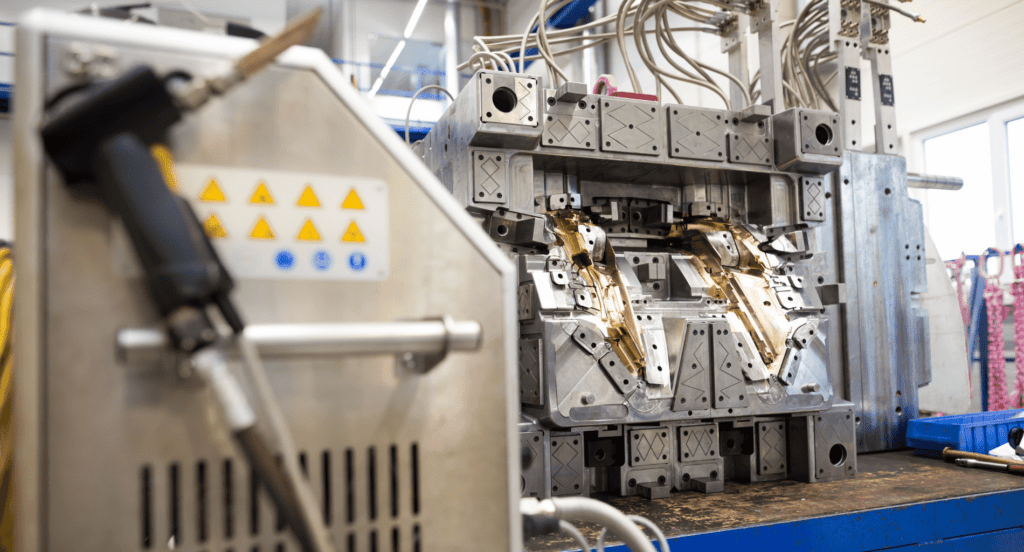
Turret Press Blanking
Turret press blanking is versatile and adaptable, allowing for rapid tool changes and accommodating a variety of shapes and sizes. This method is beneficial for short production runs and prototypes, where flexibility and quick setup are crucial. This is often used for producing complex parts with multiple cuts or bends. Zemetal provides customized turret press solutions for various businesses, ensuring efficiency and precision.
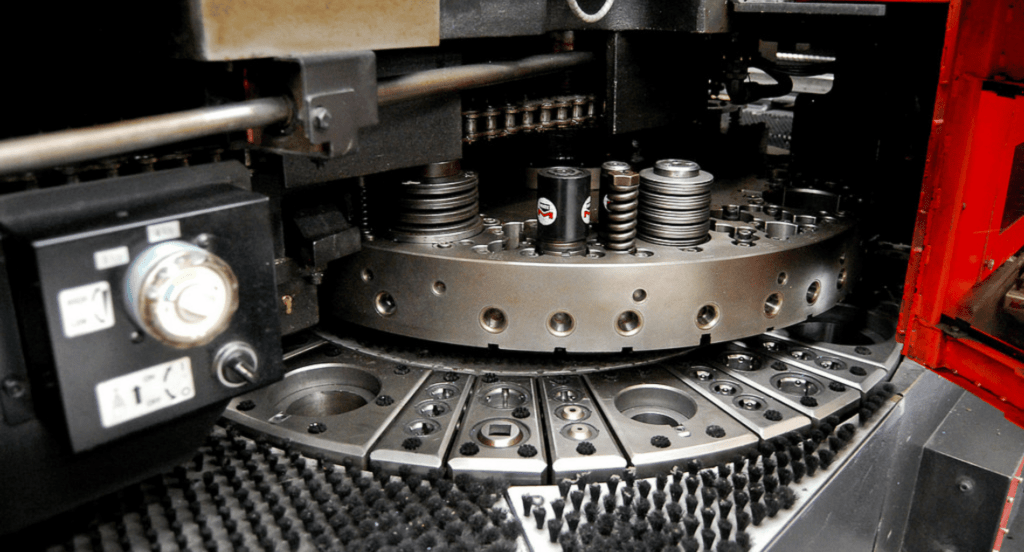
3. Materials and Tools Used in Blanking
Transitioning from the diverse types of blanking operations, it’s crucial to understand the specific materials and tools that make these processes effective. Here are the key elements:
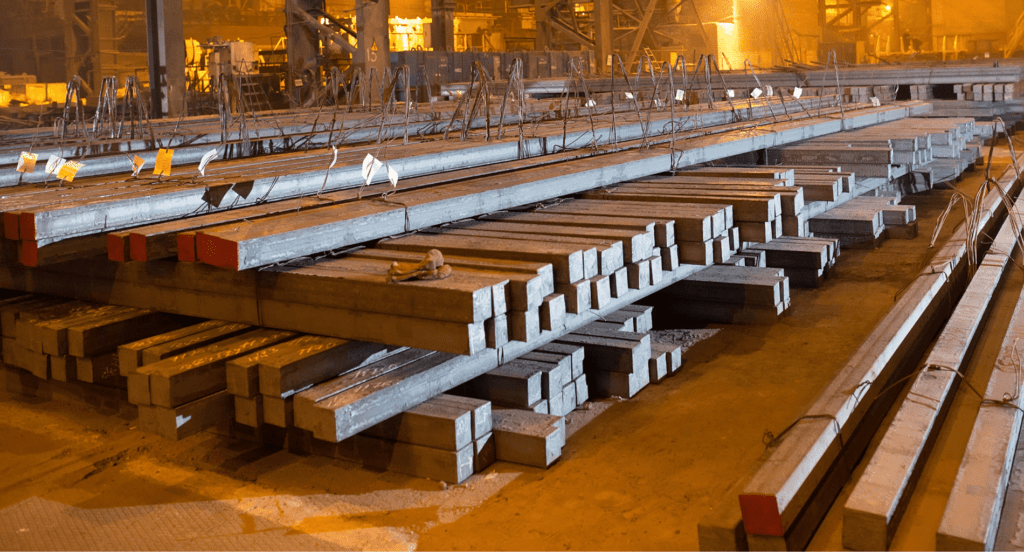
Metals for Blanking
In blanking, the choice of metal significantly influences the process’s success. Steel, aluminum, and brass are commonly used, each offering unique benefits such as durability, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. The selection is guided by factors like the intended use of the blanked part, its required strength, and specific industry standards.

Blanking Presses
Blanking presses are critical in the blanking process, applying the necessary force to cut the metal. Available in various types, including mechanical and hydraulic, they cater to different material thicknesses and production sizes. Choosing the right type is essential for achieving the precision and efficiency needed, especially in high-volume manufacturing.
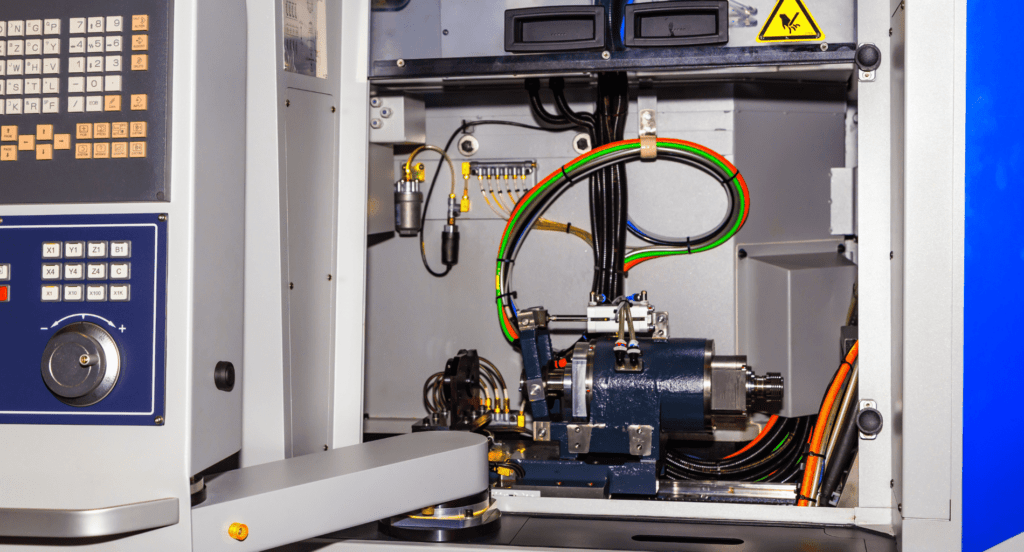
CNC Blanking Machines
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) blanking machines bring high precision and automation to the blanking process. These machines use computer programming to ensure accuracy and repeatability, making them ideal for complex and detailed designs. They are particularly valuable in industries where precision is vital, such as aerospace and electronics.
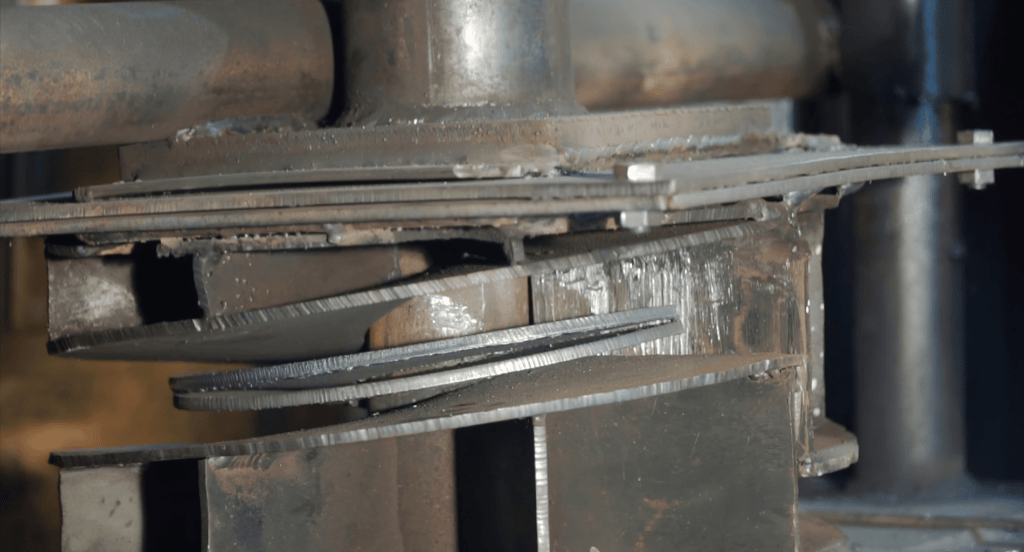
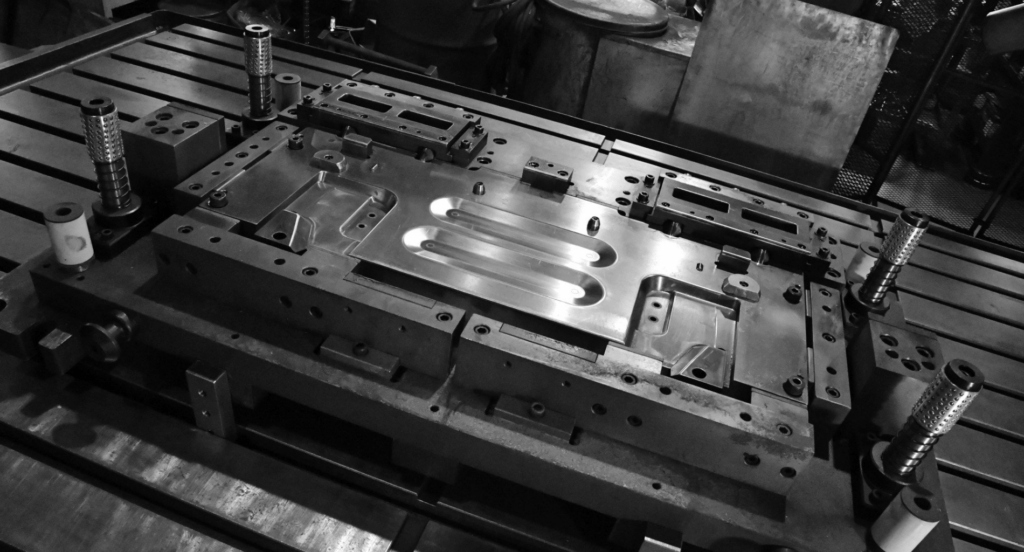
Blanking Dies
Blanking dies are custom-made tools designed to cut specific shapes from metal sheets. Their quality and precision are fundamental in determining the accuracy and finish of the final product. Made from durable materials, these dies must be precisely engineered to match the design specifications of the parts being produced.

4. The Blanking Process
After selecting the appropriate materials and tools, the focus shifts to the blanking process itself, transforming raw metals into precision components. Here are the vital steps involved in executing blanking efficiently:
Step#1 Design and Planning
The process begins with designing the part to be blanked. A detailed drawing of the part is created, specifying the shape, size, and other necessary details. Based on this design, a corresponding die is planned, which will be used to cut the metal sheet in the blanking press. This is crucial for ensuring that the die and the press will produce the exact shape required.
Step#2 Material Selection
The next step involves selecting the appropriate material for blanking. Factors like the thickness, type of metal, and other properties are considered to ensure compatibility with the design requirements. The chosen material is then prepared in sheets or coils, ready for the blanking process.
Step#3 Die Setup and Calibration
Setting up and calibrating the die is a technical and precise task. In this step, the die, which is a custom-made tool designed as per the part specifications, is set up in the blanking press. The die is carefully aligned and adjusted to ensure it matches the design dimensions accurately. This calibration is critical to achieve precise cuts and maintain consistency in the blanking process.
Step#4 Blanking Operation
During the blanking operation, the metal sheet is placed in the press, and the die comes down to cut the part out. The press applies force, causing the die to punch through the metal, creating the desired shape. This is performed with great precision to ensure the cut is clean and to the exact dimensions required. The operation is typically repeated for mass production, producing multiple identical parts.
Step#5 Quality Control
After the parts are blanked, they undergo a quality control process. Each part is inspected for dimensional accuracy, edge quality, and overall adherence to the design specifications. This ensures that every blank part meets the required standards and is suitable for its intended use. Any parts not meeting the criteria are either reworked or discarded.
5. Applications of Blanking in Various Industries
Complementing the detailed blanking process explored, it’s time to dive into the applications of blanking revealing its versatility across multiple sectors. Here are key industries where blanking plays an instrumental role:
Aerospace
In aerospace, blanking is used to manufacture components that demand high strength and light weight, such as panels and brackets. The precision of blanking is critical in ensuring the safety and functionality of aerospace parts, which must adhere to strict industry standards. It is valued for its ability to produce complex shapes with high precision.
Electronics
The electronics industry relies on blanking for creating complex components found in devices like smartphones, computers, and televisions. This process enables the production of tiny, precise parts with tight tolerances, essential for the current trend of making electronics smaller. Blanking’s efficiency and accuracy are key to meeting the fast-paced and evolving demands of this industry.
Construction
The construction industry utilizes blanking for fabricating metal components used in buildings and infrastructure, like brackets and support structures. Blanking provides the necessary precision and strength for these components, ensuring safety and durability in construction projects. Its efficiency is also key in meeting the large-scale demands of the construction industry.
6. Quality Control and Standards in Blanking
Quality control and adherence to standards are critical components in the blanking process, ensuring that the accuracy and efficiency vital in various industries are maintained. Here are the crucial aspects to consider:
Precision Measurement Technologies
The integration of advanced measurement technologies in blanking is crucial for achieving unmatched accuracy. For example, tools like laser micrometers and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) are employed to ensure that each blanked part meets exact dimensional specifications. This is critical in applications requiring tight tolerances, such as in electronic components and precision engineering.
Compliance with Specific Industry Regulations
Blanking operations must align with specific industry regulations to ensure suitability for different applications. For instance, in the automotive sector, adherence to standards like ISO/TS 16949 is essential for quality assurance. Similarly, for aerospace components, compliance with standards like AS9100 is necessary to meet the industry’s rigorous safety and quality requirements.
This table highlights the critical need for compliance with specific industry regulations and standards in blanking operations:
| Industry | Regulation/Standard | Importance |
| Automotive | ISO/TS 16949 | Ensures quality assurance and reliability in automotive parts manufacturing. |
| Aerospace | AS9100 | Meets rigorous safety and quality requirements essential in aerospace components production. |
| Medical Devices | ISO 13485 | Guarantees adherence to stringent quality management and safety standards in medical equipment manufacturing. |
| Electronics | IPC Standards | Ensures reliability and quality in the manufacturing of electronic components and assemblies. |
| Construction | ASTM International Standards | Maintains safety, quality, and performance standards in construction materials production. |
Process Control and Documentation
Implementing strict process control measures and maintaining comprehensive documentation are vital for quality assurance in blanking. This includes detailed records of machine settings, material batches, and inspection results for each production run. Such meticulous documentation not only enhances traceability but also ensures consistency in production, crucial for industries relying on high repeatability and reliability.
Surface Finish and Edge Quality Analysis
The analysis of surface finish and edge quality is a critical aspect of quality control in blanking. Techniques such as surface profilometry are used to assess the smoothness and texture of the blanked parts, while edge quality is evaluated for burrs or imperfections. Ensuring optimal surface and edge conditions is essential for parts that will be visible or require further processing, like painting or welding.
7. Advancements and Innovations in Blanking Technology
Moving beyond quality control, advancements in blanking technology are transforming metal fabrication, bridging the gap between tradition and the future. Here are some of the significant innovations:
Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology in blanking involves creating a virtual replica of the physical blanking process. This allows for real-time monitoring and simulation, enabling manufacturers to predict outcomes, optimize operations, and reduce downtime. It’s a leap forward in predictive maintenance and process improvement, ensuring higher productivity and lower operational costs.
Nano-Precision Blanking Tools
The development of nano-precision tools has taken the accuracy of blanking operations to a new level. These tools allow for extremely fine and precise cuts, ideal for industries requiring microscopic components, such as microelectronics or precision engineering. The use of such advanced tools has opened up new possibilities in manufacturing components with incredibly tight tolerances.
Laser-Assisted Blanking
Laser-assisted blanking has emerged as an innovative technique, combining traditional mechanical cutting with laser technology. This approach allows for cleaner cuts, greater flexibility in shaping materials, and reduced tool wear. It’s beneficial for complex geometries, enhancing precision while minimizing material waste. Zemetal has integrated such technology, delivering top-quality services and staying ahead in the competitive market.
Multi-Tool Blanking Stations
Advancements in multi-tool blanking stations enable operations with multiple tools in a single setup at the same time. An example of this is seen in automotive part production, where different components are blanked in one station, significantly reducing production time and increasing output. This innovation is particularly useful for high-volume manufacturing environments.
8. 3 Factors When Considering Blanking Services
After exploring the future of blanking, selecting the right service provider is essential for utilizing the full potential of this advanced manufacturing process. Here are crucial factors to consider:
#1 Quality and Precision
The provider’s ability to deliver high-quality and precise parts is critical. Evaluate their track record for consistency in product quality and adherence to dimensional accuracy. This factor directly impacts the performance and reliability of the blanked components in their end-use applications.
#2 Material Capabilities
Assess the provider’s expertise and facilities for handling different materials used in blanking. It’s essential that they can work effectively with the specific metals required for the project, whether it’s steel, aluminum, brass, or any specialty alloy. The material capabilities of the provider should align with the demands of your project to ensure optimal results.
#3 Production Volume
Consider the provider’s capacity to handle the specific production volume needs. Whether in small batches for specialized projects or large-scale production runs, the provider should demonstrate the ability to deliver without compromising on quality or efficiency. This ensures that your supply chain remains uninterrupted and cost-effective.
Conclusion
Getting precise cuts in sheet metal can be frustrating, especially when accuracy and efficiency are crucial. You need a process that consistently delivers clean, exact shapes. At Zemetal, we specialize in blanking solutions that give you the results you’re looking for.
In conclusion, this guide has explained how blanking works in sheet metal and why it’s an essential process for creating high-quality parts. If you’re ready to take your production to the next level, contact us today. Zemetal is here to provide expert blanking services tailored to your needs.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








