Have you ever considered how integral sheet metal parts are to your business operations? These components are the backbone of countless products and structures, playing a pivotal role in the metal fabrication industry.
As a seasoned expert in metal fabrication, I bring a wealth of knowledge and experience to the table. My insights are grounded in years of hands-on involvement in the industry, ensuring that the information I share is relevant and reliable.
Sheet metal parts are remarkable for their durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Their application spans a wide array of industries, making them an essential element in modern manufacturing and construction.
In this guide, we will delve into the various aspects of sheet metal parts, covering their types, down to its best practices in their use. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the field, this guide promises to enhance your understanding and utilization of these crucial components.
Read on to discover the world of sheet metal parts.
1. Basic Overview of Sheet Metal Parts
Sheet metal parts are fundamental components used in various industries, from automotive to construction. These parts are created by cutting and bending metal sheets, a process that allows for high precision and versatility. Common materials include steel, aluminum, brass, and copper, each chosen for its unique properties like strength, conductivity, or corrosion resistance.
The beauty of sheet metal lies in its adaptability and efficiency in production. Techniques like stamping, bending, and cutting are employed to shape these sheets into desired forms. This adaptability makes sheet metal parts suitable for a wide range of applications, from intricate electronic components to large architectural structures.
2. Types of Sheet Metal Materials
Building on the basic overview of sheet metal parts, it’s important to understand the variety of materials used in their fabrication. Here are the different sheet metal materials catering to specific industry needs:
- Steel: Steel is one of the most common materials used in sheet metal fabrication due to its strength and durability. It’s an alloy primarily made of iron and carbon, offering high resistance to wear and tear. Steel is ideal for heavy-duty applications and is commonly used in the automotive and construction industries.
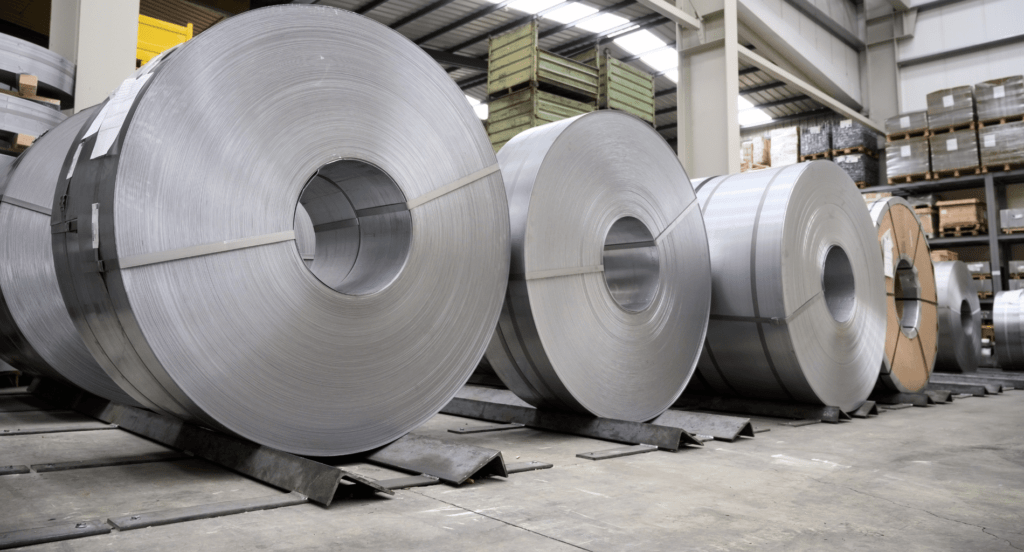

- Aluminum: Aluminum stands out for its lightweight yet strong nature. It’s highly malleable, which makes it easy to work with in manufacturing processes. Aluminum resists corrosion well, making it a popular choice for aerospace and marine applications.

- Copper: Copper is known for its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It’s often used in electrical components and roofing materials. Copper also develops a unique patina over time, which can add aesthetic value to architectural projects.
- Brass: Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is notable for its corrosion resistance and acoustic properties. This material is widely used in musical instruments like trumpets and saxophones. In sheet metal fabrication, brass is often chosen for decorative purposes due to its gold-like appearance.

3. Design Considerations for Sheet Metal Parts
Transitioning from the types of materials, it’s crucial to focus on the design considerations for sheet metal parts. Here are key factors that significantly impact the functionality of these components:
Bend Radius
The bend radius is a crucial aspect of design, especially for sheet metal. It’s important to ensure that the bend radius is at least equal to the thickness of the sheet metal to avoid cracking or material failure. The material’s ductility determines the minimum bend radius it can withstand without damage. Zemetal carefully considers these factors in their metal fabrication processes to ensure optimal results.
Hole Placement and Size
When designing sheet metal parts, the placement and size of holes are critical. Holes should be placed at a distance of at least the material’s thickness from the edge of the sheet to maintain structural integrity. Also, the diameter of the holes should not be smaller than the thickness of the metal to prevent distortion during fabrication.
Cutting and Joining Methods
The methods used for cutting and joining sheet metal impact the design. Techniques like laser cutting, welding, and riveting require specific design considerations. For instance, if welding is used, adequate space for welding seams should be included in the design. The right cutting and joining methods are the key to flawless and functional designs.
Material Properties and Compatibility
Different materials behave differently under stress, heat, and during bending processes. It’s important to choose a material compatible with the intended fabrication process and final application of the part. For example, stainless steel is resistant to corrosion and heat, making it suitable for parts exposed to harsh environments.
4. Fabrication Processes of Sheet Metal Parts
Moving from design considerations, the fabrication of sheet metal parts is a multi-step process that transforms raw materials into functional components. Each step plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of the final product. Let’s explore its process:
Step#1 Cutting
Cutting is the first step in sheet metal fabrication. It involves slicing large sheets into smaller, workable pieces or specific shapes. Techniques like shearing, laser cutting, and waterjet cutting are used, depending on the material and required precision. This process sets the foundation for the subsequent fabrication steps.
Step#2 Bending
After cutting, bending shapes the metal into the desired form. This is typically done using press brakes or other bending machines. The bending process must consider factors like bend radius and material springback to achieve accurate angles. It’s crucial for creating complex shapes and angles in sheet metal parts.
Step#3 Joining
Joining is essential for assembling multiple pieces of sheet metal. Techniques like welding, riveting, and the use of adhesives are employed based on the requirements of the project. This step requires precision to ensure strength for durable joints. To address this, Zemetal employs expert techniques to ensure high-quality and long-lasting assemblies in their projects.
Step#4 Forming
Forming involves altering the shape of the metal sheet without removing any material. Processes like stamping or roll forming are used to create specific contours, textures, or patterns on the metal surface. This step is vital for adding functional or aesthetic characteristics to the part.
Step#5 Finishing
The final step in the fabrication process is finishing. This includes treatments like sandblasting, painting, or powder coating to improve the appearance, resistance to corrosion, or surface texture of the metal part. Finishing not only enhances the product’s aesthetic appeal but also extends its lifespan by protecting it from environmental factors.
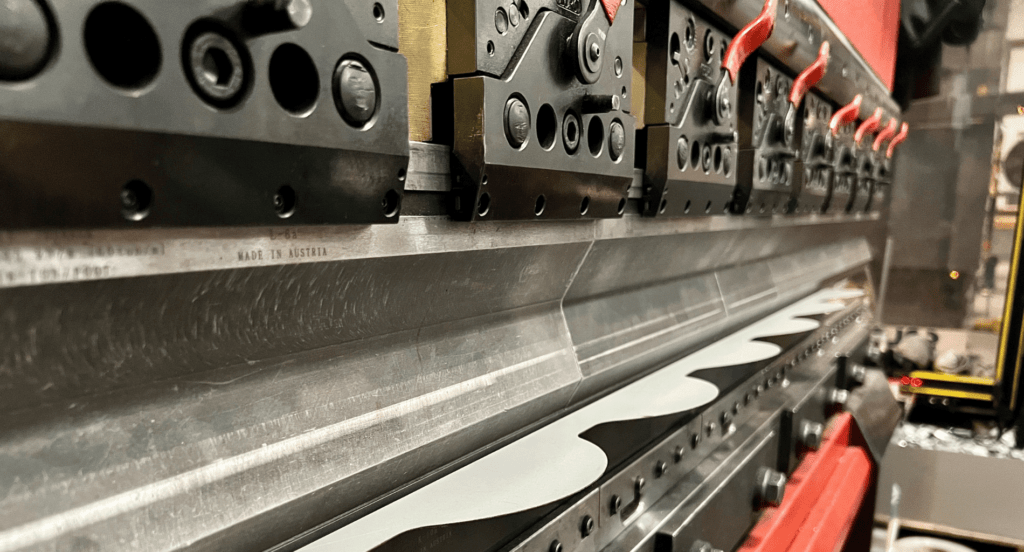
5. Applications of Sheet Metal Parts in Various Industries
Following the exploration of fabrication processes, it’s evident that sheet metal parts have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the industries where sheet metal parts play a crucial role:
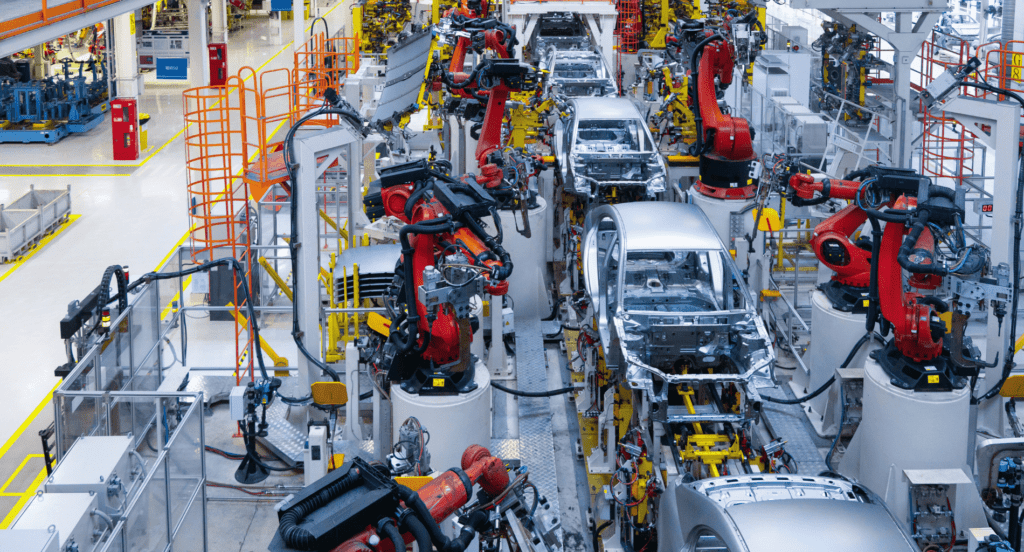
Automotive Industry
As the automotive market, expected to grow at a CAGR of 2.79% from 2022 to 2028 according to Industry Research, the use of sheet metal remains fundamental. In this industry, sheet metal is crucial for body panels, frames, and engine components, owing to its ability to be molded into complex shapes and its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Thus, contributing to the production of durable vehicles in this rapidly growing sector.
Construction and Architecture
The construction and architecture industries heavily rely on sheet metal for structural elements, roofing, and decorative features. Its durability and resistance to environmental factors make it ideal for building exteriors and support structures. Sheet metal is also used for aesthetic purposes, offering architects a versatile material for creative and functional designs.

Aerospace and Defense
Sheet metal parts are critical in aerospace and defense for their lightweight and high-strength properties. Components like fuselage panels, wings, and internal support structures in aircraft are often made from advanced sheet metal alloys. This ensures the aircraft are both robust and light, essential for flight efficiency and safety in these high-stakes industries.
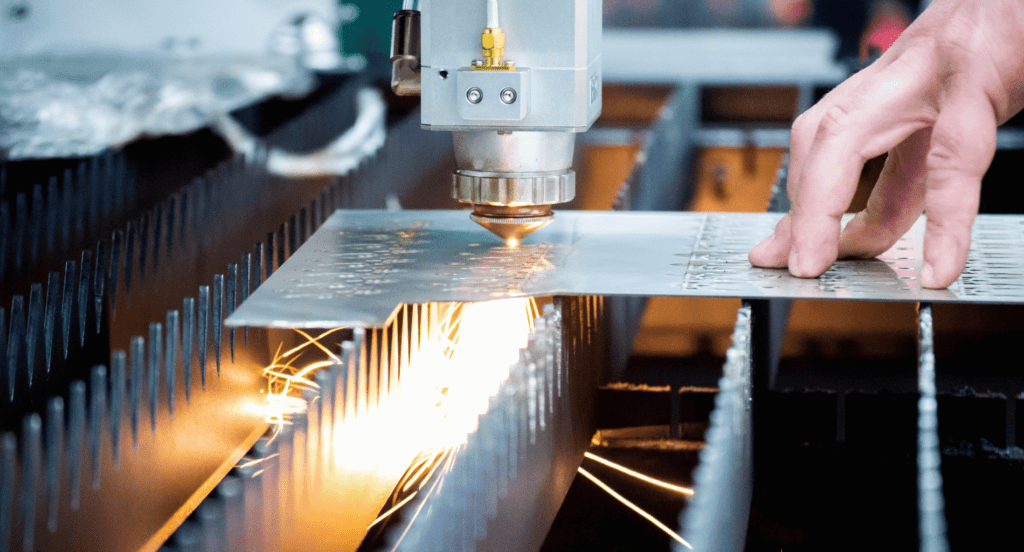
6. Innovations in Sheet Metal Technology
As we’ve seen the diverse applications of sheet metal parts in various industries, it’s clear that ongoing innovations in sheet metal technology are driving these sectors forward. Here are some of the remarkable innovations in this field:
3D Printing for Metal
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized the way sheet metal parts are produced. This technology allows for the creation of complex, lightweight structures that were previously impossible or too costly to manufacture. It enables designers to prototype rapidly and customize parts with precision, leading to more efficient and flexible production processes.
Hybrid Fabrication Techniques
Hybrid fabrication techniques, which combine traditional methods with modern technologies, are emerging as a significant innovation. For example, combining traditional welding with laser-based techniques or integrating additive manufacturing with conventional subtractive methods like milling. These hybrid approaches allow for greater versatility, as well as improved efficiency and precision in the fabrication of sheet metal parts.
This table outlines various hybrid fabrication techniques, describing their combination of traditional and modern methods and emphasizing the resulting benefits in terms of versatility, efficiency, and precision in fabricating sheet metal parts and other components.
| Hybrid Technique | Combination | Benefits |
| Welding and Laser-Based Techniques | Combining traditional welding with advanced laser-based methods. | Enhances precision, speed, and quality of the welding process. |
| Additive and Subtractive Manufacturing | Integrating 3D printing (additive) with traditional milling or machining (subtractive). | Allows for complex geometries and efficient material usage, resulting in more intricate and customized parts. |
| Forging and CNC Machining | Merging traditional forging with CNC machining for finishing. | Combines the strength and durability of forged parts with the precision of CNC machining. |
| Casting and 3D Scanning | Using 3D scanning in casting processes for accurate mold creation. | Improves the accuracy and speed of mold production, leading to higher-quality cast parts. |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication and Automation | Incorporating automated processes in traditional sheet metal fabrication. | Increases efficiency, consistency, and productivity in sheet metal part production. |
Smart Factory Integration
The integration of sheet metal fabrication processes with smart factory technologies is revolutionizing the industry. This includes the use of IoT sensors, AI-driven process optimization, and automated quality control systems. These technologies enhance efficiency, reduce errors, and enable real-time monitoring, leading to higher quality products and more efficient operations.
Conclusion
Through this guide, we’ve illuminated the essentials of sheet metal parts, equipping businesses with crucial knowledge for their ventures. This insight paves the way for more informed decisions in utilizing sheet metal in various applications.
If your business is looking to delve deeper into sheet metal solutions, Zemetal is here to guide you. Contact us for tailored expertise and support in navigating the world of sheet metal parts.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








