Considering the best finishing process for all metal products? Understanding the key differences between powder coating vs galvanizing is a big step to make an informed decision.
Drawing from extensive industry experience, we will provide an expert comparison to help you go through these two popular methods.
While powder coating offers a wide range of colors and finishes, galvanizing is known for its exceptional durability and corrosion resistance. Each method serves distinct purposes, applications, and requirements.
In this ultimate guide, we will explore in-depth insights into the processes, benefits, costs, and applications of both powder coating and galvanizing, helping to align your choice with the business needs.
Read on to delve deeper into the world of metal finishes.
1. Overview of Industrial Finishing Techniques
Industrial finishing techniques play an important role in enhancing the durability and aesthetic appeal of metal products. These methods not only provide protection against environmental factors like corrosion and wear but also offer a means to infuse products with visual appeal, aligning them with brand aesthetics and industry standards.
Among the large number of finishing techniques available, powder coating and galvanizing stand out due to their unique properties and applications. Powder coating, a process involving the electrostatic application of a dry powder, which is then cured under heat, offers a remarkable range of colors and finishes. It’s favored for its environmental friendliness and versatility in applications ranging from automotive to furniture.
Galvanizing, on the other hand, involves dipping metal into molten zinc, creating a robust, corrosion-resistant coating. Its reliability in harsh conditions makes it a go-to for outdoor structures and industrial applications. Each technique holds its advantages, shaping the choice based on the specific needs of a project.
2. Powder Coating: An Overview
Powder coating, a distinctive industrial finishing technique, stands as a contemporary alternative to traditional liquid painting. This process involves applying a dry powder, typically a mixture of finely ground particles of pigment and resin, onto a surface. Unlike liquid paint, it doesn’t require a solvent, hence the coating is applied electrostatically and then cured under heat.
Types of Powder Coating:
- Epoxy Powder Coating: Known for its superb chemical resistance, epoxy powder coatings are ideal for indoor applications. They provide a hard, durable finish, but tend to fade under prolonged UV exposure. A common example is the coating used on metal furniture.
- PolyesterPowder Coating: This type excels in outdoor durability, offering excellent resistance to UV rays and weathering. Polyester coatings are often seen on outdoor furniture and automotive parts.
- AcrylicPowder Coating: Acrylic coatings stand out for their clarity and gloss retention. They provide a smooth finish and are typically used for automotive parts and consumer electronics. As per Volza, there are 221 active Acrylic powder coating exporters in the world exporting to 226 Buyers.
- Urethane Powder Coating: Urethane coatings are known for their strong resistance to abrasion and impact. They maintain color and gloss well over time, making them suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
Advantages:
- Environmental Friendliness: Generates less waste and harmful emissions compared to liquid coatings, aligning with eco-friendly practices.
- Durable Finish: Offers excellent resistance to chipping, scratching, and corrosion, ensuring longevity.
- Cost-Effective: Efficient material usage and lower energy requirements make it a cost-effective option.
- Aesthetic Flexibility: Provides a wide range of colors and textures, allowing for creative and custom finishes.
- Thicker Coatings without Running or Sagging: Enables the application of thicker coatings without the risk of drips or sags, common in liquid coatings.
Disadvantages:
- Limited to Conductive Materials: Primarily suitable for metal substrates, limiting its use on non-conductive materials.
- Color Change Challenges: Color changes during the process can be time-consuming, impacting production efficiency.
- Complex Shapes Challenge: Coating uniformity can be difficult on complex shapes or with intricate designs.
- High Initial Setup Cost: The initial investment for equipment and setup is higher compared to traditional liquid painting.
- Not Ideal for Thin Films: Achieving ultra-thin coatings is more challenging than with liquid coatings, limiting its use in certain applications.
3. Galvanizing Explained
Galvanizing, a fundamental process in metal protection, involves coating steel or iron with a layer of zinc. This process, known as hot-dip galvanizing, is achieved by immersing the metal in a bath of molten zinc. Zemetal services understands that the resultant zinc coating forms a barrier that protects the underlying metal from corrosion. Galvanizing is known for its long-lasting protection, particularly in outdoor and industrial areas.
Types of Galvanizing:
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing: The most common form, where metal is submerged in molten zinc. It provides a thick, durable coating ideal for large structures like bridge support.
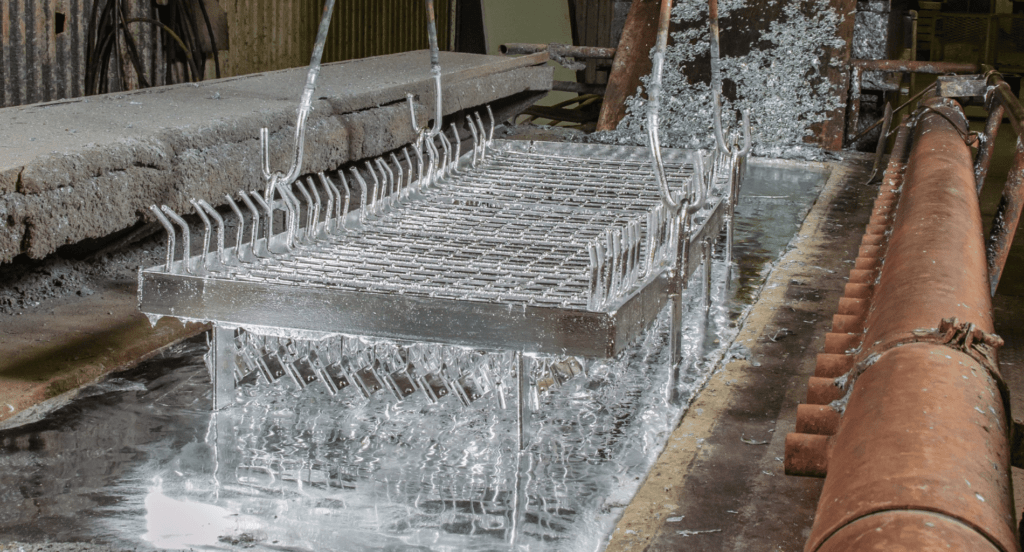

- Electrogalvanizing: A process where zinc is applied using an electrical current. It offers a thinner, more precise coating, often used for small parts in automotive manufacturing.
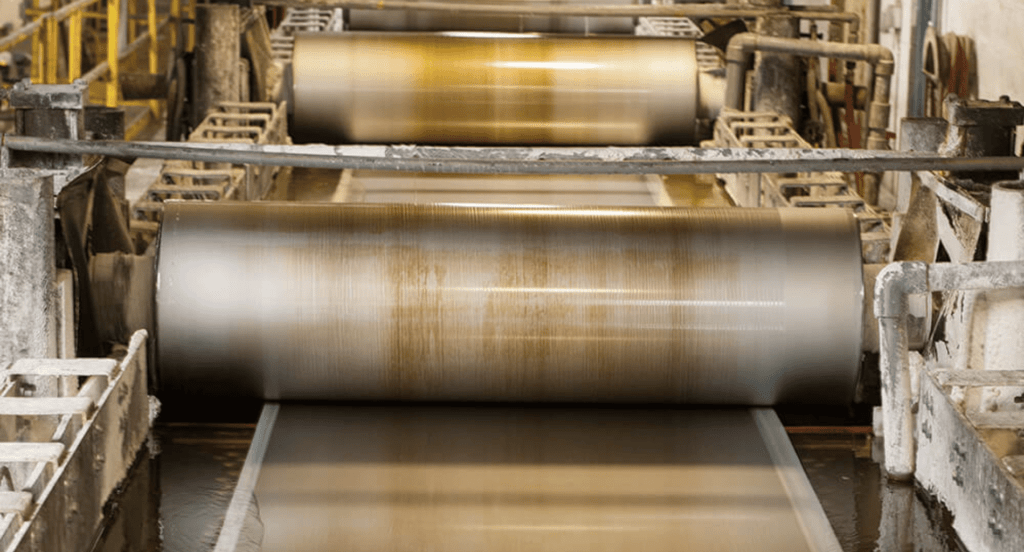

- Sherardizing: Involves heating steel in zinc powder, creating a zinc-iron alloy. It’s used for small, complex parts, providing uniform coverage.
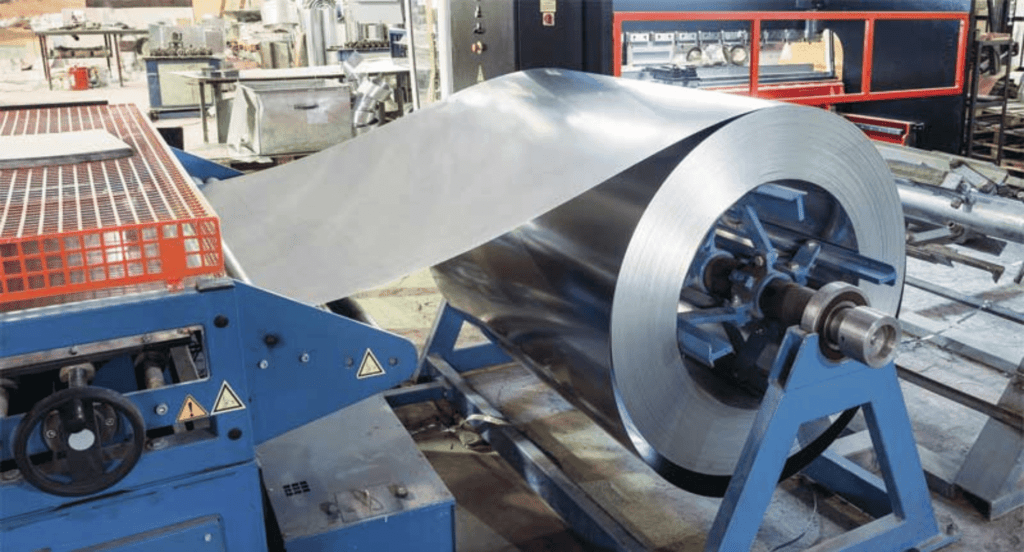
- Pre-Galvanizing: Steel is galvanized during the manufacturing process, ensuring consistent coverage. Commonly used in the manufacturing of steel profiles and sheets.
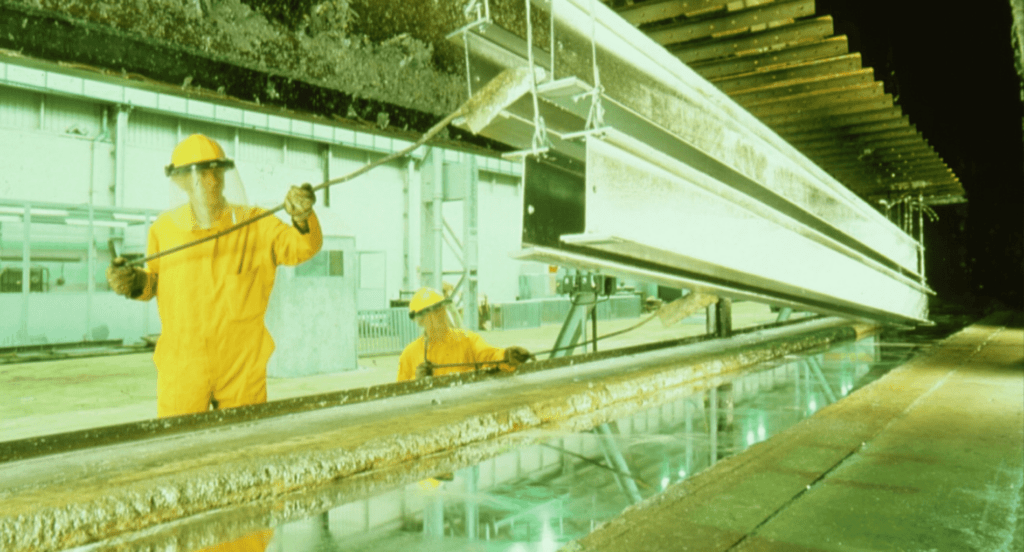
Advantages of Galvanizing:
- Long-Term Protection: Offers superior corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environmental conditions.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal upkeep over its lifespan, reducing long-term costs.
- Economical: Generally more cost-effective than other long-term protective coatings.
- Full Coverage: Ensures complete protection, even in joints, recesses, and other hard-to-reach areas.
- Reliability: The process is simple and controllable, yielding consistent, high-quality results.
Disadvantages of Galvanizing:
- Appearance Limitations: Galvanization offers limited aesthetic options, generally resulting in a standard matte gray finish. For example, galvanized steel used in industrial shelving often features this distinctive, uniform gray appearance.
- Size Restrictions: Large structures may be challenging to galvanize due to the size limitations of galvanizing baths.
- Thickness of Coating: Can be uneven, especially around edges and corners.
- Welding Challenges: Galvanized steel requires special welding techniques and safety precautions due to zinc fumes.
- Potential for Distortion: Thin steel sections can warp due to the high temperature of the molten zinc bath.
4. Powder Coating vs. Galvanizing: Key Difference
Having delved into the specifics of both powder coating and galvanizing, it’s clear that each method offers unique benefits and challenges. To further clarify their distinctions and help in making a more informed decision for your industrial needs, see the following detailed comparison.
| Aspect | Powder Coating | Galvanizing |
| Material Application | Electrostatically applied dry powder | Molten zinc bath immersion |
| Finish Variety | Wide range of colors and textures | Typically a standard matte gray finish |
| Substrate Suitability | Primarily metals, particularly conductive ones | Best suited for steel and iron |
| Environmental Impact | Lower VOC emissions, more eco-friendly | Generates waste, potential environmental concerns |
| Durability | High resistance to chipping and scratching | Superior corrosion resistance, especially outdoors |
| Application Process | Requires curing in an oven | No curing required; cools naturally |
| Cost | Can be more costly due to process and materials | Generally more cost-effective |
| Thickness of Coating | Uniform and can be thick without running | Can vary, thicker at corners and edges |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance but can be difficult to repair | Very low maintenance, self-healing |
| Aesthetic Flexibility | High flexibility in aesthetic finishes | Limited aesthetic options |
| Heat Resistance | Varies by type, generally good heat resistance | Excellent heat resistance |
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Powder Coating and Galvanizing
Having explored the key differences between powder coating and galvanizing, it becomes evident that each method has its own unique set of advantages and considerations. Here are the critical factors to consider:
#1 Project Requirements and Durability Needs
When selecting between powder coating and galvanizing, understanding the specific needs of your project is crucial. Powder coating provides a wide range of aesthetic finishes and is highly suitable for projects requiring specific color matching or a unique appearance. On the other hand, galvanizing is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for products exposed to harsh outdoor environments.
#2 Budget
Budget is always a key consideration. Generally, powder coating can be more expensive due to its elaborate process and the materials used. Galvanizing, in contrast, is often more cost-effective, especially for large-scale or bulk projects. Zemetal services offers competitive pricing options for both processes, ensuring cost-effectiveness without compromising on quality.
#3 Aesthetic Preferences
Aesthetic preferences play a significant role in the choice between powder coating and galvanizing. Powder coating offers a wide range of colors and finishes, from high gloss to matte, making it ideal for projects where visual appeal is a priority. Galvanizing, while limited in color options, provides a distinctive metallic sheen that can be desirable for an industrial look.
Conclusion
To summarize, this guide has thoroughly compared powder coating and galvanizing, equipping you with essential insights to make an informed choice for every metal finishing process. The right decision aligns with understanding the specific benefits and limitations of each method to every business project’s demands.
For expert guidance and top-quality services in both powder coating and galvanizing, look no further than Zemetal. For more information or to discuss your project, feel free to contact us today.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








