Are you weighing the benefits of powder coating and anodizing for your next project? Selecting the right finish can significantly impact both the performance and aesthetics of your metal products.
With years of expertise in metal finishes, we bring a wealth of practical, industry-tested knowledge to guide you through making the right choices for your business.
Both powder coating and anodizing serve to protect and beautify metal surfaces; however, powder coating offers extensive color choices and a strong finish, whereas anodizing excels in providing corrosion-resistant and highly durable surfaces.
In this guide, we’ll thoroughly explore and compare both powder coating and anodizing, examining their applications, pros, and cons, to arm you with the information needed for an informed choice.
Read on for essential insights into these processes.
1. Importance of Surface Finishes in Various Industries
Surface finishes such as powder coating and anodizing are integral to enhancing the performance and longevity of metal products in various industries. Here are key aspects demonstrating their importance:
- Facilitating Easy Maintenance and Cleaning: Surface finishes, like powder coating, simplify metal product maintenance. They offer smooth, low-maintenance surfaces, particularly valuable in hygiene-sensitive sectors like healthcare and food services, saving time and resources.
- Enhancing Environmental Resistance: Surface finishes in industries like construction and transportation improve resistance to UV, moisture, and chemicals for longer-lasting, high-performance products. Zemetal, with its expertise in surface finishes, offers industry-specific solutions for durability and aesthetics.
- Improving Aesthetics and Brand Image: Aesthetic appeal is crucial for consumer choices and brand differentitation. Powder coating, with its varied colors and textures, offers brand customization, particularly important in consumer-facing industries where visuals affect marketability.
- Ensuring Product Safety and Compliance: In industries like medical and food processing, surface finishes are vital for safety and compliance. For instance, in the food and beverage industry, anodizing ensures food-grade metal equipment stays corrosion-resistant and non-toxic, preventing contamination.
2. Understanding Powder Coating
Powder coating is a sophisticated finishing process where dry powder is electrostatically applied to a surface and then cured under heat to form a hard, protective layer. Renowned for its durability and environmental friendliness, it releases minimal volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a sustainable choice. This method offers a wide range of colors and finishes, catering to diverse industrial and consumer applications.
Applications of Powder Coating
- Automotive Industry: Powder coating is used in the automotive industry for its exceptional durability and resistance to harsh conditions. Components such as frames, wheels, and undercarriage parts are commonly treated with powder coating to withstand wear and tear, and to maintain their aesthetic appeal over time.
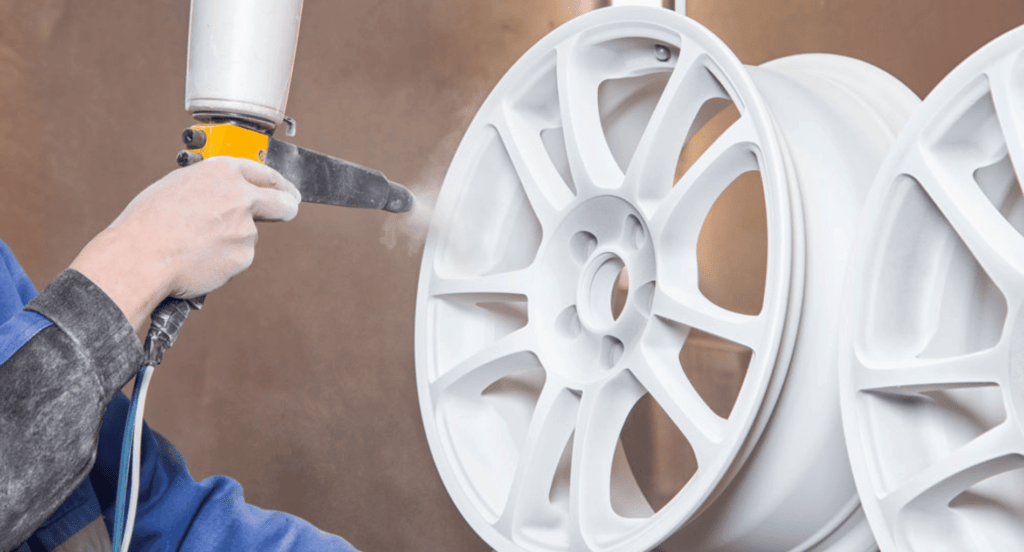
- Consumer Electronics: In consumer electronics, powder coating is known for its aesthetic versatility and protective qualities. It’s used for items like computer cases and home appliances, offering a durable finish that resists scratches and corrosion while providing a modern, stylish look.

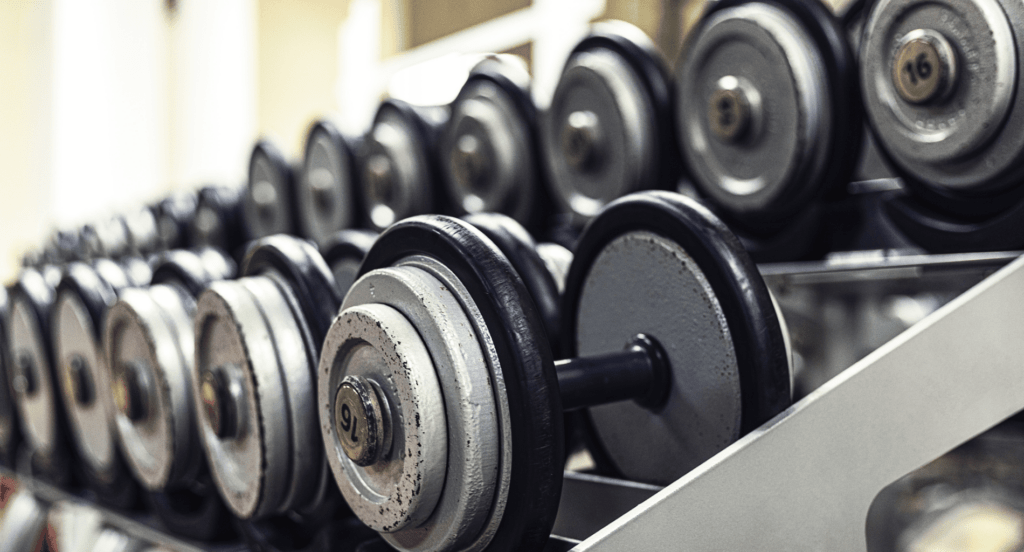
- Outdoor and Sporting Equipment: Outdoor and sporting equipment manufacturers rely on powder coating for its ability to endure extreme weather conditions and rough handling. This finish is ideal for items like bicycles, gym equipment, and outdoor furniture, providing long-lasting protection and vibrant color retention.

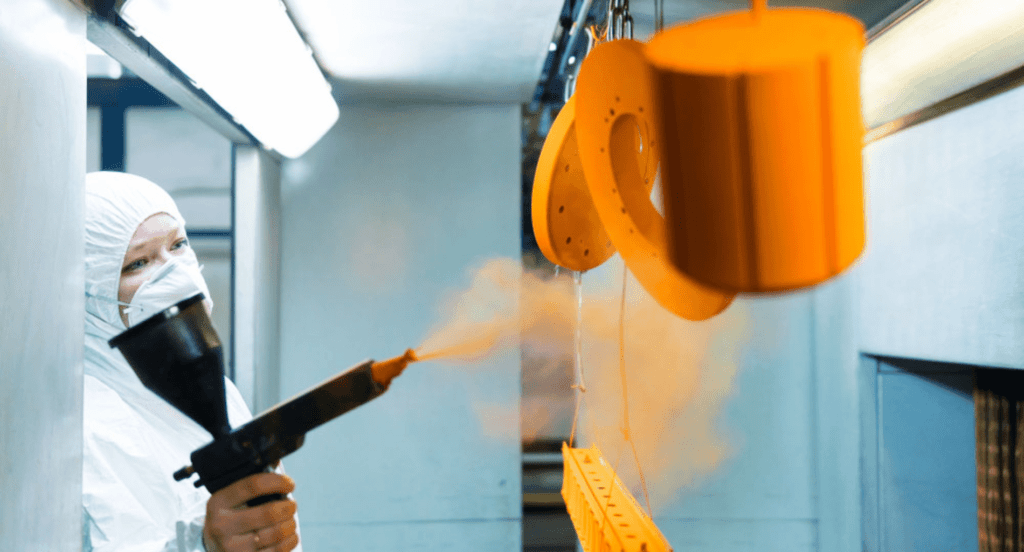
- Architectural and Construction: Architectural elements and construction materials benefit greatly from powder coating. For example, this finish enhances durability and appearance of window frames, metal panels, and outdoor structures while resisting environmental elements.
Advantages of Powder Coating
- Environmental Sustainability: Powder coating stands out for its eco-friendliness. Unlike traditional liquid paints, it doesn’t contain harmful solvents or release significant amounts of VOCs, making it a safer choice for the environment.
- Enhanced Durability: It offers exceptional durability with a hard, scratch-resistant layer that maintains its finish, even in tough conditions.
- Economic Efficiency: It is cost-effective for large-scale production due to its efficient process and minimal waste. Excess powder can be reused, reducing costs.
- Uniform Application: Powder coating creates a smooth, uniform surface without drips or runs that are often seen in liquid paints. This uniformity is particularly advantageous for complex geometries and parts with detailed designs.
Disadvantages of Powder Coating
- Limited Finish Thinness: Achieving thin finishes in powder coating can be challenging, especially when fine detailing or ultra-thin layers are required in applications. Industries requiring precision thin coatings may find powder coating less suitable.
- High Initial Setup Costs: Setting up a powder coating facility requires a significant initial investment. The cost of equipment, such as curing ovens and spray booths, can be expensive for small businesses or startups, making it less accessible compared to some other finishing processes.
- Sensitivity to External Conditions: Powder coatings are sensitive to external conditions like humidity and temperature during application. Variations in these factors can affect the quality of the finish, requiring controlled environments for consistent results, which can be challenging to maintain.
- Limited Application on Heat-Sensitive Materials: Powder coating’s high-temperature curing process can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials and limits its application to metals unable to handle the required heat levels.
3. Exploring Anodizing
Anodizing is a specialized electrochemical process, primarily for aluminum, enhances its oxide layer, boosting corrosion resistance. It involves placing metal in an acid bath, applying electricity, creating a hardened surface that can be dyed for aesthetics. As per Verified Market Research, metal anodizing market will grow at 4.1% CAGR from 2023 to 2030, due to demand for lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials in various industries.
Applications of Anodizing
- Energy Sector: Within the energy sector, anodizing is used to protect components against environmental wear. This includes solar panel frames and wind turbine parts, where durability and resistance to weather elements are crucial.
- Marine Equipment: Anodizing is essential in the marine industry for protecting equipment from harsh sea conditions. It’s widely used for items like boat hulls, railings, and masts, offering superior resistance to saltwater corrosion and sun exposure.
- Military and Defense: In the military and defense sector, anodizing is applied to various equipment, from firearms to vehicular components. This treatment enhances the metal’s resistance to corrosion and wear, crucial for reliability and durability in challenging field conditions.
- Medical Equipment: In the medical field, anodizing is used for surgical instruments, implants, and other equipment. Its non-toxic nature and resistance to sterilization processes make it a safe and reliable choice for medical applications.
Advantages of Anodizing
- Corrosion Resistance: The anodizing process provides a protective layer that greatly enhances a metal’s resistance to corrosion. This feature is especially beneficial in environments exposed to moisture and corrosive elements, ensuring the metal’s longevity.
- EnhancedElectrical Insulation: Anodizing effectively increases the electrical insulation of metals. This characteristic makes it ideal for electronic applications where non-conductive properties are essential.
- Thermal Insulation Enhancement: The anodizing process increases a metal’s resistance to heat, reducing the risk of damage in high-temperature environments. This is important for components used in settings where heat exposure is frequent, ensuring their durability and functional integrity.
- Health and Safety Compliance: Anodizing is a safe process, producing no harmful or toxic substances. It complies with various health and safety regulations, making it a preferred choice in industries where such compliance is non-negotiable.
Disadvantages of Anodizing
- Limited Color Options: Anodizing offers a more limited color range compared to powder coating. Colors tend to be less vibrant, which may not suit projects requiring bold or highly specific colors.
- SubstrateSpecificity: Anodizing is primarily effective on aluminum and certain non-iron metals, making it less versatile and limiting its applicability across various industries. Businesses working with a wide range of metals might find this a restrictive aspect.
- Wear and Fade Over Time: Anodized finishes, although durable, may wear or fade over time, particularly in harsh environments or high-traffic areas. This can impact both the metal’s appearance and protective properties, necessitating maintenance or re-treatment.
4. Comparative Analysis: Powder Coating vs. Anodizing
After understanding powder coating and anodizing, exploring their differences reveals distinct advantages and limitations in their application. Here are critical areas of comparison between these two finishing processes:
Application Process and Efficiency
- Powder Coating: Thisrequires a specific setup, including a spray booth and curing oven, which can be costly to install. However, once set up, it is highly efficient for large batches, with quick turnaround times.The ability to recycle unused powder makes it a cost-effective solution in the long run.
- Anodizing: This is an electrolytic process, necessitating specialized equipment and safety measures due to the chemicals involved. It’s highly efficient for treating aluminum but is limited to conductive materials. The process is generally slower than powder coating, particularly for thicker anodized layers.
Thickness and Coverage
- Powder Coating: This typically results in a thicker and more durable layer, offering strong protection and a fuller appearance. This thickness is beneficial for hiding surface imperfections on metals. However, it might not be suitable for projects requiring very thin or lightweight finishes.
- Anodizing: This produces a much thinner coating compared to powder coating, ideal for precision parts where dimensions are critical. This thinness also preserves the original texture and detail of the metal surface. However, it may offer slightly less physical protection than the thicker powder coating layer.
Suitability for Different Metals
- Powder Coating: It is versatile, applicable to various metals like steel, aluminum, and iron, even some non-metal surfaces. It employs electrostatic application for even coverage on complex shapes. However, properly preparing and treating the metal surface is vital for coating adhesion and durability.
- Anodizing: This is primarily used for aluminum, enhancing the metal’s natural properties. It is less versatile than powder coating, which can be used on a wider range of metals. For metals other than aluminum, different processes or coatings are needed to achieve similar protection and aesthetics.
Chemical Resistance
- Powder Coating: Powder coatings are generally resistant to many common chemicals, making them suitable for industrial applications where exposure to solvents is likely, but their effectiveness depends on the formulation. Specialized coatings may be required for extreme chemical environments.
- Anodizing: The anodized layer offers excellent resistance to many chemicals, particularly acidic substances. This resistance makes it ideal for use in environments where corrosion from chemical exposure is a concern. However, anodizing might be less effective against alkaline substances.
5. 4 Tips for Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Transitioning from the comparison between powder coating and anodizing, when selecting between these two several factors must be considered to ensure the best finish for every project. Here are key aspects to consider:
#1 Material Compatibility
The compatibility between the chosen finishing process and the material of the project is critical. Different metals respond uniquely to powder coating and anodizing, affecting the final outcome’s quality and durability. Therefore, it’s important to match the finishing process with the metal’s properties to ensure optimal adherence, appearance, and longevity of the finish.
This table explores the relationship between various finishing processes and different metals, highlighting how compatibility affects the quality, appearance, and longevity of the final product.
| Metal Type | Finishing Process | Compatibility Considerations | Outcome Impact |
| Aluminum | Anodizing | Excellent adherence, enhances corrosion resistance | High durability, aesthetic appeal |
| Steel | Powder Coating | Good adherence, provides thick and even coverage | Robust finish, long-lasting color |
| Copper | Powder Coating | Requires specific preparation for effective adherence | Unique aesthetic, prone to variations |
| Stainless Steel | Anodizing | Limited compatibility, requires specialized process | Variable results, often challenging |
| Titanium | Anodizing | Good compatibility, enhances natural oxide layer | Enhanced corrosion resistance, color variety |
#2 Production Volume and Efficiency
Consider the scale and efficiency of the production. Powder coating is highly efficient for large batches, due to its quick application and curing times, boosting production speed. While anodizing, it is more suited for smaller or specialized batches where its unique qualities add significant value to the product. Zemetal’s expertise guarantees efficient and high-quality application, regardless of the batch size or production demands.
#3 Budget Considerations
The budget is a crucial factor in the decision-making process. Powder coating tends to be more cost-effective, especially for larger projects, due to its efficiency and the recyclability of excess powder. Anodizing, while sometimes more expensive, offers a long-lasting finish that can be a wise investment for projects requiring extended durability and minimal maintenance.
#4 Environmental Impact and Compliance
Consider the environmental implications of the finishing choice. Powder coating is an environmentally friendly option, with fewer VOC emissions, making it a greener choice. Anodizing, while also relatively eco-friendly, requires careful waste management due to the chemicals involved. If environmental compliance is a top priority, this can greatly impact the choice for the suitable surface finishing.
Conclusion
Both powder coating and anodizing stand as crucial finishing techniques, each with distinct advantages and applications. This guide has provided valuable insights designed to help you simplify decision-making processes, ensuring best results for your metal fabrication projects.
For those seeking expert guidance and services in metal finishes, Zemetal offers unmatched expertise and solutions. Contact us to discover how we can assist with your metal fabrication needs and elevate your projects.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








