Is flux core sheet metal welding the key to more efficient metal fabrication? Absolutely, and it’s transforming the industry with its superior capabilities.
As a metal fabrication expert with years of hands-on experience, I’m here to guide you through the complexities of flux core welding.
The world of flux core sheet metal welding is vast and filled with potential. It’s a technique that promises improved productivity and quality, making it a vital skill for any serious fabricator.
In this guide, we’ll unravel the secrets to mastering flux core sheet metal welding, from its fundamental concepts to advanced application techniques.
Read on to transform your approach to metal fabrication.
1. Understanding the Basics of Flux Core Welding
Flux core welding, a semi-automatic or automatic arc welding process celebrated for its speed and versatility, is increasingly gaining traction in the industry. Its distinct use of a tubular wire filled with flux eliminates the need for shielding gas, broadening its application in various environments. This method is not only highly valued for its strong, durable bonds on thicker metals but also for its adaptability and efficiency.
Notably, the global flux cored welding wire market is on a significant upward trajectory, expected to reach USD 2275.5 million by 2027, according to LinkedIn. Such growth underscores its widespread adoption and the trust many industries place in this technology for quality welds, even in challenging scenarios. Understanding the basics and market’s rising trust in flux core welding is essential for its effective use.
2. Advantages of Flux Core Welding in Sheet Metal
Building on the understanding of flux core welding’s basics, it’s evident this method offers significant advantages when applied to sheet metal fabrication. Here are some key benefits worth noting:
Improved Efficiency
Flux core welding is known for its high-speed welding capabilities, significantly reducing project timelines. The process allows for a continuous feed of wire, meaning longer welds can be made without interruption. This efficiency is particularly advantageous in high-volume production environments where time is a critical factor. In automotive manufacturing, the ability to quickly join sheet metal components is invaluable.
Superior Penetration
With its deep penetration, flux core welding excels in joining thicker pieces of metal with ease. This characteristic ensures strong, robust welds that are crucial for the structural integrity of any fabrication. In industries where safety and durability are paramount, such as construction, this deep penetration translates into reliable, long-lasting structures.
Cost-Effectiveness
Flux core welding can be more cost-effective compared to other methods. The equipment required is generally less expensive and more portable, and the need for fewer consumables, such as shielding gas, reduces ongoing costs. Additionally, the high welding speed means less labor time is required, further contributing to cost savings. This economic efficiency makes flux core welding ideal for budget-conscious small businesses.
3. Flux Core Welding Techniques for Sheet Metal
Perfecting the art of flux core welding on sheet metal requires a deep dive into specific techniques. Here, we’ll explore two essential strategies that significantly impact the quality and efficiency of welding projects:
Stringer Bead Technique
The stringer bead technique in flux core welding involves moving the welding gun in a straight line with minimal weaving. This method is ideal for creating strong, narrow welds on sheet metal, particularly in positions where space or access is limited. An example of its application is welding seams on thin metal sheets, where a concentrated and controlled bead is necessary.
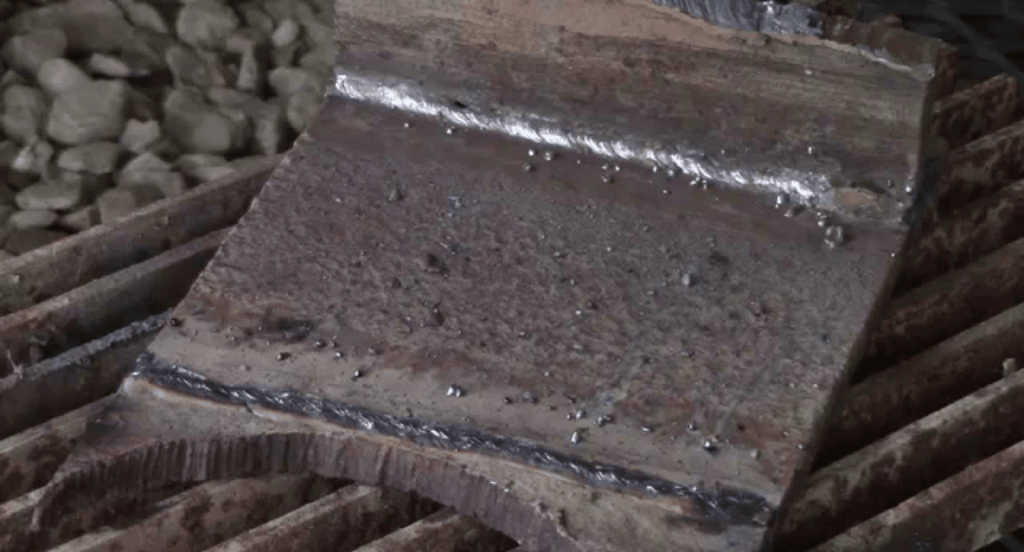

Forehand Technique
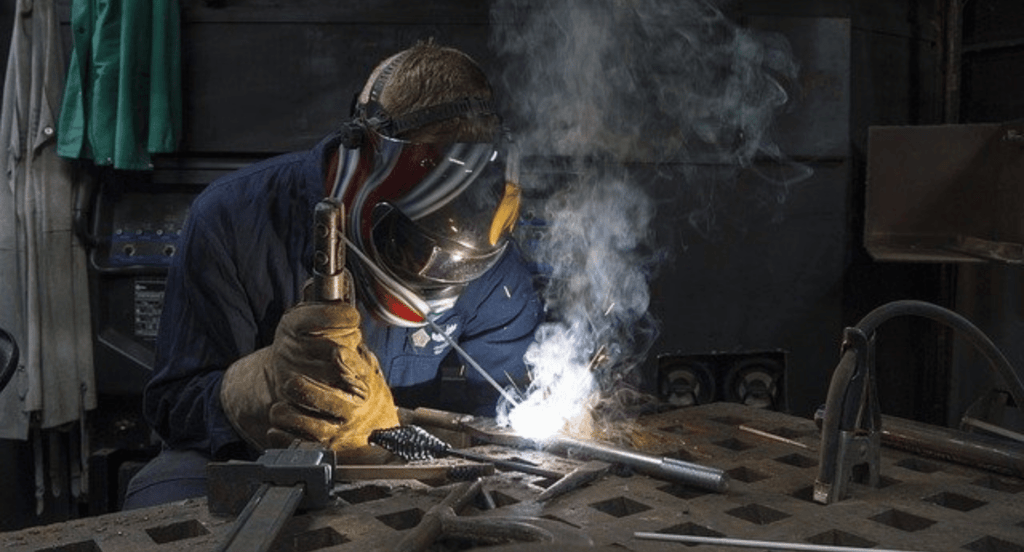
In the forehand technique, the welding gun is angled towards the direction of welding, allowing the welder to see the puddle and the seam ahead. This approach in flux core welding is useful for thinner metals, as it provides better control over the weld pool, allowing for cleaner, more precise welds. It’s a technique that I find particularly useful for detailed work where precision is key.

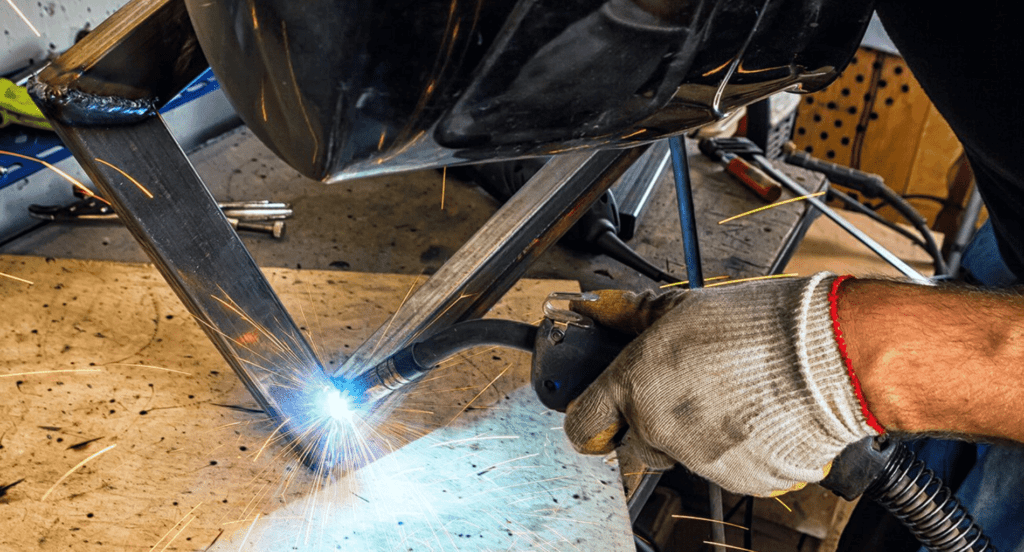
Backhand Technique
The backhand technique, utilized in flux core welding, involves pointing the gun back towards the completed weld. This method is effective for deeper penetration, making it suitable for thicker pieces of sheet metal. Zemetal harnesses this technique for applications needing robust welds, enabling increased heat concentration and metal penetration. The backhand method excels in projects demanding structural strength.

4. Step-by-Step Guide to Flux Core Welding Process
Following on the journey of flux core welding requires a structured approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide designed to navigate through the process, ensuring a robust and efficient welding experience:
Step#1 Setting Up the Equipment
First step, ensure all welding equipment is properly set up. This includes assembling the welding gun, connecting the power source, and loading the flux core wire. Checking for any wear or damage on the components is crucial for safety and performance. A properly maintained setup ensures a seamless welding experience with minimal disruptions.
Step#2 Preparing Metal
Next prepare the sheet metal by removing any rust, paint, or debris, cleanliness is key in welding. This can involve grinding or using a wire brush. Clean metal ensures better electrical conductivity and a stronger weld. It’s always satisfying to see how a well-prepared surface leads to a superior weld.
Step#3 Choosing the Right Parameters
Once preparation done, select the correct voltage, amperage and wire feed speed. These settings vary based on the thickness and type of metal being welded. For example, thinner metals require lower heat settings to prevent burn-through. Testing on scrap pieces before starting the actual work can help dial in the perfect settings.
Step#4 The Welding Technique
Then, hold the welding gun at a 10-15 degree angle and use a steady, consistent motion to create the weld. The technique might differ slightly between dragging (pulling the gun towards you) or pushing (pushing the gun away from you), depending on the desired penetration and bead shape. Like, dragging is often used for deeper penetration on thicker materials.
Step#5 Post-Welding Cleanup
After welding, it’s common to have slag covering the weld, which needs to be chipped away and brushed off for a clean finish. Inspecting the weld for any defects and making necessary touch-ups is also part of this final step. Proper cleanup and inspection ensure the durability and appearance of the weld meet high standards.
5. Applications of Flux Core Welding in Various Industries
Having outlined the step-by-step flux core welding process, it’s intriguing to see its practical applications unfold across different sectors. Let’s delve into this versatile welding technique that is making a substantial impact in various industries:
Oil and Gas Industry
Flux core welding is critical in the oil and gas industry, particularly in pipeline construction and maintenance. Its ability to provide strong, durable welds is essential for pipes that transport oil and gas over long distances. In constructing major pipelines, flux core welding swiftly and effectively joins sections, securing a continuous resource flow. This application highlights the technique’s importance in energy infrastructure.
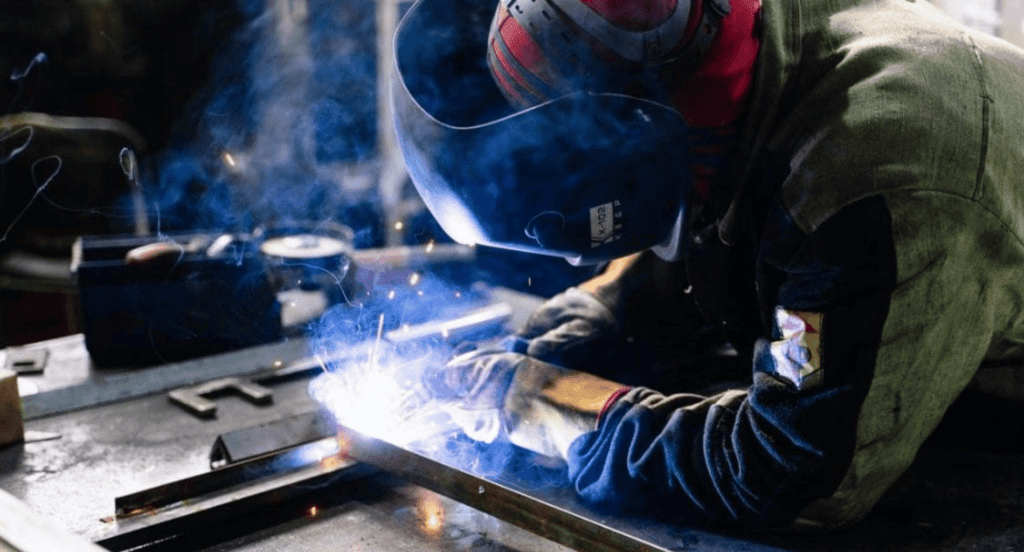

Automotive and Transportation Industry
The automotive industry relies on flux core welding for assembling vehicles and their components. Its ability to produce strong welds quickly is essential for meeting production demands. From the chassis to the engine components, flux core welding is utilized for its efficiency and strength. In this fast-paced industry, the speed and reliability of flux core welding are highly valued.
Construction and Infrastructure Industry
In the construction industry, flux core welding is critical for building solid frameworks and structures. It’s regularly utilized for assembling bridges, towering buildings, and expansive commercial projects where the integrity of welds is paramount. Zemetal enhances this process by offering top-tier expert guidance, ensuring every weld contributes to the enduring strength and safety of these substantial construction projects.
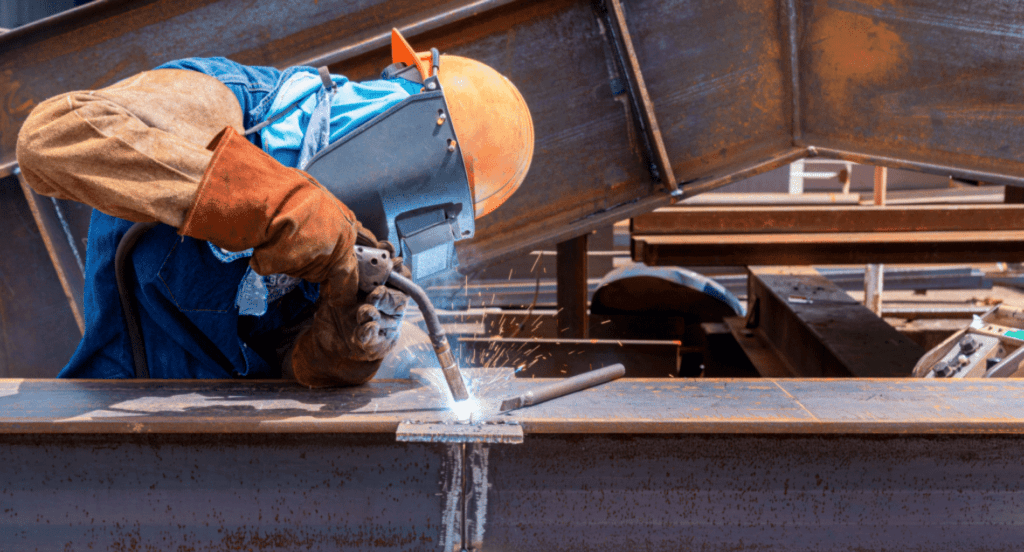

6. Common Challenges and Solutions in Flux Core Welding
Navigating through the world of flux core welding involves facing some common challenges. Let’s explore these issues and find effective solutions to ensure a smoother welding experience:
Heat Control Difficulties
Managing the right amount of heat is a delicate balance; too much can cause warping, while too little leads to poor penetration. This is particularly tricky with thinner materials that are sensitive to temperature variations. Implementing a gradual approach to adjusting heat settings helps identify the sweet spot for each material. It’s also beneficial to use a welding machine with reliable digital controls for precise temperature management.
Inconsistent Arc Stability
An unstable arc can lead to uneven welds and is often caused by improper settings or external factors like wind. This inconsistency can significantly affect the quality and appearance of the weld. To mitigate this, regularly calibrates the welder and using high-quality consumables can lead to a more stable arc. Shielding the welding area from drafts can enhance stability, ensuring consistent quality in each weld.
Wire Feeding Issues
Inconsistent wire feeding disrupts the welding process, leading to irregular welds. Common causes include worn-out drive rolls, incorrect tension, and liner blockages. To address this, regular maintenance and cleaning of the welding apparatus are vital. Ensuring compatibility between drive rolls and wire type, along with correct tension, resolves feeding issues for a uniform and reliable weld.
The table below outlines the common causes of inconsistent wire feeding in welding processes and their solutions, highlighting the importance of maintenance and correct equipment setup for optimal welding performance.
| Cause | Solution |
| Worn-out drive rolls | Replace with compatible drive rolls for wire type |
| Incorrect tension | Adjust tension to match wire specifications |
| Liner blockages | Regular cleaning and inspection of the liner |
| Incompatibility of wire and drive rolls | Ensure wire type matches drive roll design |
| Lack of regular maintenance | Implement routine maintenance and cleaning schedules |
7. Advancements and Innovations in Flux Core Welding
While addressing common challenges in flux core welding offers valuable insights, it’s equally important to look forward. Here, we’ll delve into some of the significant advancements and innovations shaping the future of this welding technique:
Enhanced Wire Formulations
The development of new wire formulations has significantly improved flux core welding. These new wires offer better stability, increased strength, and higher efficiency. They’ve been tailored to produce less spatter and provide more consistent arc stability, which are critical for high-quality welds. It’s exciting to witness how these advancements directly translate to smoother operations and better end products.
Automated Welding Systems
Automation in flux core welding is transitioning the industry. Automated systems are now capable of handling detailed welding tasks with precision and consistency. These systems offer improved speed, accuracy, and repeatability, which are vital for large-scale production and complex projects. The integration of advanced sensors and control technology ensures each weld is performed to the highest standard.
Enhanced Arc Performance
Innovations in power supply and control technology have significantly enhanced arc performance in flux core welding. Newer systems offer more stable arcs, even at lower voltages, improving the quality of welds on thinner materials and reducing spatter. This leads to smoother finishes and stronger, more reliable joints.
Conclusion
Through this exploration of flux core welding, it’s clear that mastering this skill can significantly elevate the standards and efficiency of any fabrication work. This guide has aimed to provide the insights and knowledge necessary to navigate this complex field successfully.
Dive deeper into the world of welding with Zemetal’s expertise and resources at your side. For more information and personalized assistance, contact us today — let’s craft excellence together.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








