Why is copper electroplating crucial in modern metal fabrication? Copper electroplating enhances durability and electrical conductivity in various components.
With extensive experience in metal fabrication, we offer insights that can transform every business operation into the next level.
Copper electroplating is a method where a layer of copper is deposited on a surface using electrical currents. This process enhances the product’s quality and durability, playing a key role in metal fabrication.
In this guide, you’ll discover the intricacies of copper electroplating, its benefits, and how it can be effectively applied in your business.
Continue reading to fully equip copper electroplating in your metal work.
1. Understanding Copper Electroplating
Copper electroplating deposits a thin copper layer on metal surfaces using electric current, known for its high conductivity and corrosion resistance. With Precedence Research forecasting the global copper market’s growth from USD 304.2 billion in 2022 to USD 497.86 billion by 2032, the relevance of copper electroplating in industrial applications is more significant than ever. It’s a fascinating field that’s constantly evolving.
This process involves immersing the metal workpiece in a copper sulfate solution and applying an electric current, which causes copper ions to bond to the surface of the workpiece. This method not only enhances the electrical properties of the metal but also improves its appearance and durability. Given its increasing market value and widespread use, understanding copper electroplating is crucial for businesses in metal fabrication.
2. Advantages of Copper Electroplating
After exploring the basics of copper electroplating, it’s clear that this process offers numerous benefits. This technique boosts metal part functionality and longevity. Key advantages of copper electroplating include:
Improved Electrical Conductivity
Copper electroplating significantly increases the electrical conductivity of metal parts, making them ideal for electrical applications. This enhanced conductivity is crucial for components in electronics and power transmission. The process ensures a consistent and efficient electrical connection, reducing energy loss and improving performance.
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
A layer of copper provides excellent protection against rust and corrosion, ensuring the longevity of the metal. This is particularly valuable in harsh environments, such as marine or industrial settings. Copper’s ability to resist environmental factors helps maintain the structural integrity and appearance of the metal over time. It’s incredible how copper turns vulnerable metals into enduring champions against nature’s challenges.
Increased Heat Tolerance
Copper-coated components, using common copper plating methods, can withstand higher temperatures, making them suitable for heat-intensive environments. This quality is essential in automotive and aerospace industries, where parts are regularly exposed to high heat. The copper layer acts as a thermal barrier, protecting the underlying material from degradation.
Better Adhesion for Further Coatings
Copper electroplating creates a smooth surface that is ideal for additional coatings or treatments. This is important for metals requiring multiple layers, such as in protective coatings or paint finishes. The initial copper layer enhances the adherence and effectiveness of subsequent coatings, leading to a more durable and long-lasting product.
3. Copper Electroplating Techniques
Following the advantages of copper electroplating, it’s essential to understand the various techniques used in this process. Different methods cater to varied needs, ensuring optimal outcomes. Here are some of the techniques:
Barrel Electroplating
Ideal for small parts, this method involves placing components in a rotating barrel filled with electroplating solution. It ensures even coating and is cost-effective for high-volume production. The rotating motion allows for uniform coverage, reducing the risk of uneven spots. Zemetal Fabrications often chooses this method for its efficiency in processing bulk orders with consistent quality.
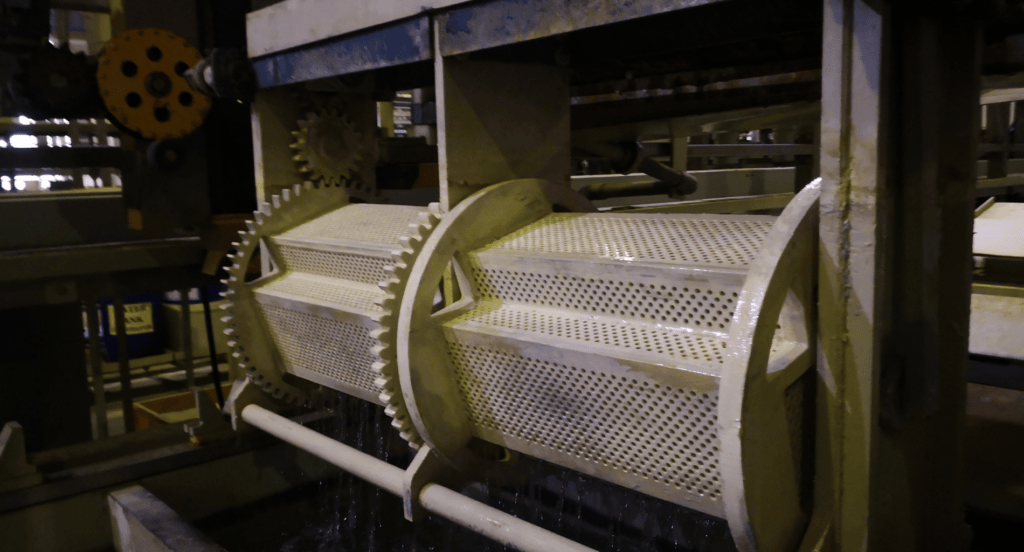

Rack Electroplating
Used for larger or more delicate parts, this technique involves affixing items to a rack before submerging them in the plating solution. It provides precise control over the plating thickness and quality. This approach is particularly useful for intricate designs, as it prevents damage during the plating process. Rack electroplating is favored for its precision and quality results on complex parts.
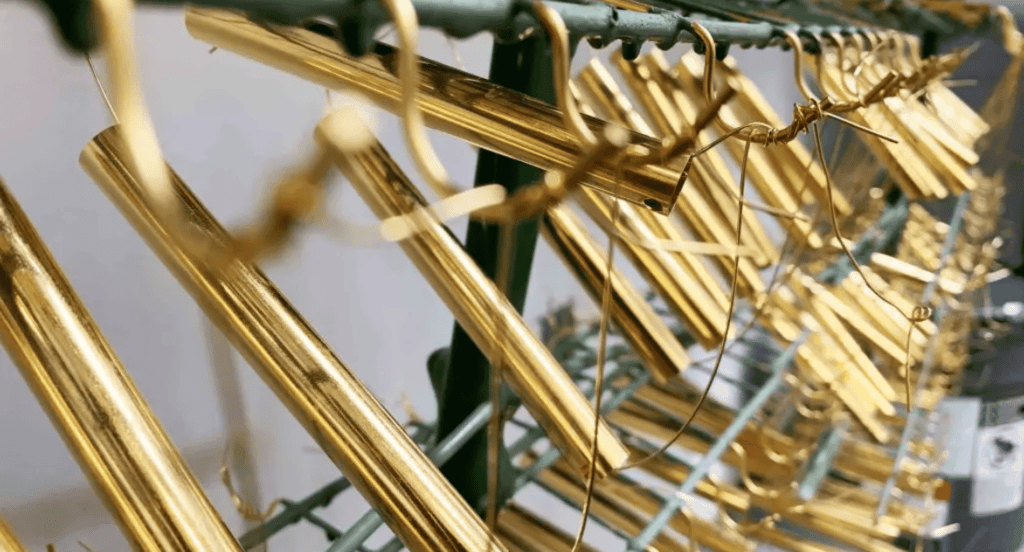
Brush Electroplating
This method is perfect for selective plating or repairs. A plating solution is applied with a brush, allowing targeted application on specific areas without immersing the entire part. It’s ideal for touch-ups or adding details to already plated pieces. Brush electroplating offers a high level of control and minimal wastage of materials.
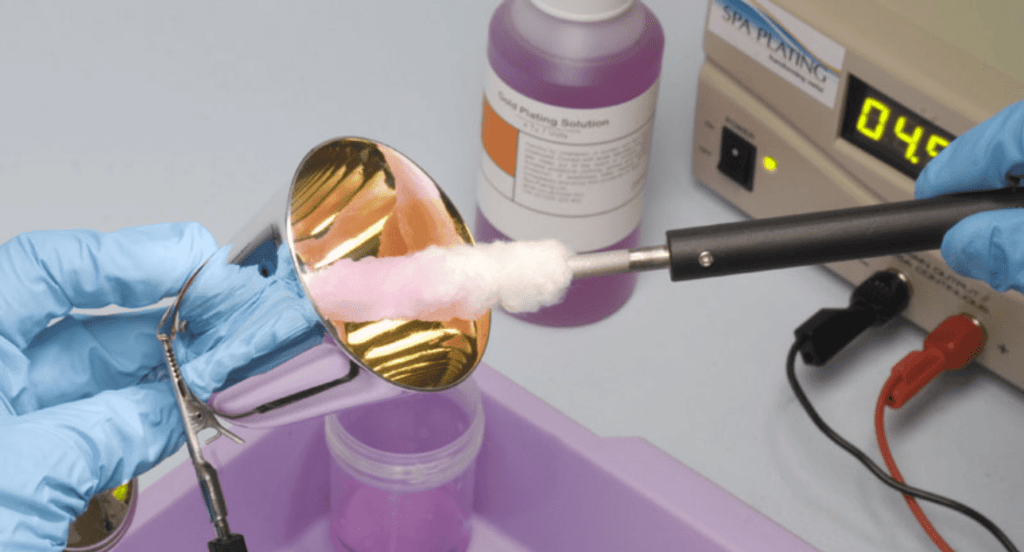
Continuous Electroplating
Suitable for wires and strips, this technique involves running the material through a continuous plating solution, ideal for high-speed and large-scale production. It’s efficient for long, continuous materials, ensuring a consistent coating throughout. Continuous electroplating is key in industries requiring long, uniformly plated components.

Vibratory Electroplating
Similar to barrel plating but uses vibratory motion to ensure uniform coating, especially effective for intricate or oddly-shaped parts. The vibratory action helps to reach all crevices and surfaces evenly. This method is particularly useful for components with complex geometries that require thorough coverage. It’s like giving each unique part its own customized, perfect finish.
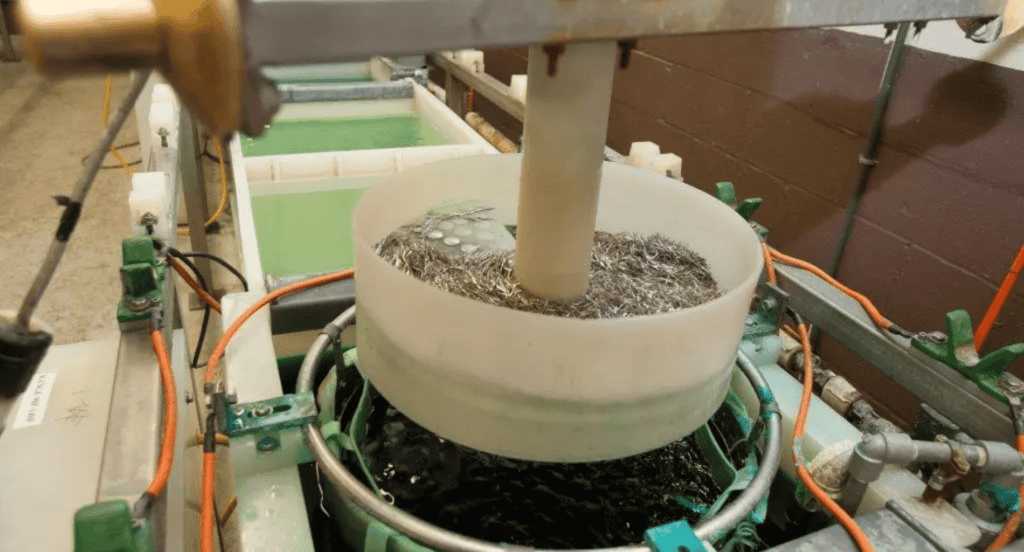
4. Step-by-Step Guide to the Copper Electroplating Process
After delving into the various techniques of copper electroplating, it’s essential to understand the step-by-step process involved. Let’s simplify the process for all. Here are the steps in the copper electroplating process:
Step#1 Surface Preparation
The metal surface is cleaned thoroughly to remove any impurities or oxides. This may involve degreasing, pickling, or sandblasting to ensure a clean and receptive surface for plating. Removing all contaminants is crucial for a successful electroplating outcome, as any residue can lead to poor adhesion or defects. This step sets the foundation for the quality of the final plated product.
Step#2 Bath Preparation
A solution of copper sulfate and sulfuric acid is prepared. The concentration and pH of the bath are carefully controlled to suit the specific electroplating requirements. The solution’s consistency is key to ensuring uniform copper deposition and overall quality of the electroplating. Regular monitoring and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal bath conditions.
Step#3 Mounting and Immersion
The metal item is mounted on a rack or placed in a barrel, then immersed in the electroplating bath. Proper positioning ensures even plating coverage. The way the item is mounted can significantly affect the plating results, with careful attention needed to avoid areas of high or low current density. This step is essential for achieving consistent and uniform copper layers.
Step#4 Electroplating
An electric current is applied, causing copper ions in the solution to deposit onto the metal surface. The duration and current density determine the thickness of the copper layer. The electroplating process requires precise control of current and time to achieve the desired plating thickness and quality. This phase is critical in defining the electrical and physical properties of the plated layer.
Step#5 Finishing and Drying
After achieving the desired thickness, the item is removed from the bath, rinsed, and dried. A final inspection ensures quality and adherence to specifications. The finishing step is vital to prevent any post-plating oxidation or tarnishing, and a thorough inspection guarantees that the electroplating meets all required standards and specifications. This final phase ensures the longevity and effectiveness of the copper plating.
5. Industrial Applications of Copper Electroplating
Following the detailed process of copper electroplating, it’s fascinating to explore its diverse industrial applications. Copper electroplating is vital in many industries. Key applications include:
Electronics and Electrical Components
Copper electroplating is extensively used in the electronics industry for circuit boards and electrical connectors. Its superior conductivity ensures efficient power distribution and signal transmission in devices. This method is crucial for minimizing energy loss and enhancing the performance of electronic products. It’s also key in producing reliable and long-lasting components, critical in today’s technology-driven world.

Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, copper electroplating is utilized for components like radiators, brake lines, and electrical connectors. It enhances durability and heat resistance, vital for vehicle performance. The use of copper plating in automobiles contributes to safety and efficiency, particularly in high-stress parts. It’s a testament to copper’s versatility and strength in demanding environments.

Aerospace and Defense
Copper plating is critical in aerospace and defense for components that require robustness and reliability. It’s used in satellite components, aircraft electrical systems, and military hardware. The reliability provided by copper plating is essential in these high-stakes fields where failure is not an option. Zemetal Fabrications relies on this process to meet the stringent standards required in aerospace and defense projects.
Jewelry and Decorative Items
Copper electroplating adds aesthetic appeal to jewelry and decorative items. It provides a beautiful finish and also serves as a base for additional metal plating. The elegance and versatility of copper make it a favorite in the design world, offering both beauty and functionality. It allows for creative expression while ensuring the durability of the items.

6. Challenges and Solutions in Copper Electroplating
After exploring the diverse applications of copper electroplating, it’s important to address the challenges faced in this process and the solutions to overcome them. Below are the some of the challenges and solutions:
Uneven Coating Thickness
Implement precise control of the electroplating parameters, such as current density and bath composition. Regular monitoring and adjustments ensure consistent thickness across the plated surface. Using advanced technology for real-time monitoring can further enhance precision. Additionally, training personnel in fine-tuning these parameters can greatly improve the consistency of the coating.
Effective electroplating relies on precise control and monitoring of parameters, as summarized in the table below.
| Control Strategy | Description |
| Parameter Adjustment | Precise control of current density and bath composition to maintain consistent plating thickness. |
| Regular Monitoring | Monitoring and adjustments to ensure uniformity and consistency across the plated surface. |
| Real-time Technology | Utilizing advanced technology for real-time monitoring to enhance precision and control. |
| Personnel Training | Training personnel in fine-tuning parameters to improve coating consistency and quality. |
| Quality Control Protocols | Implementing protocols for stringent quality control to maintain desired plating standards. |
Adhesion Issues
Enhance surface preparation techniques, including thorough cleaning and proper activation of the base metal. This ensures a clean and reactive surface for better copper adhesion. Employing advanced cleaning methods like ultrasonic cleaning can be more effective. For example, using ultrasonic cleaning in automotive parts ensures deeper removal of contaminants before plating.
Copper Bath Contamination
Regularly filter and purify the electroplating bath to remove impurities. Maintaining a clean bath is crucial for quality plating results. Incorporation of filtration systems that continuously clean the bath can prevent contamination buildup. Additionally, routine analysis of the bath composition helps in early detection and rectification of impurities.
Excessive Energy Consumption
Optimize the electroplating process through efficient power supply units and by minimizing the distance between anodes and cathodes. This reduces energy consumption and increases process efficiency. Implementing energy recovery systems can also reduce overall energy costs. It’s amazing how smart tweaks in the process can lead to such significant energy savings.
7. 5 Factors to Consider in Copper Electroplating
Following the discussion of challenges and solutions, it’s crucial to consider specific factors that impact the copper electroplating process. These factors are essential for quality results and efficient electroplating. Key considerations include:
#1 Quality of Base Metal
The purity and condition of the base metal greatly affect the electroplating outcome. Metals with impurities or defects may lead to poor adhesion and uneven coating. Using metals with high purity levels and minimal structural flaws is recommended for optimal plating. Pre-treatment processes like buffing and polishing can also improve the base metal’s suitability for electroplating.
#2 Electroplating Bath Composition
The concentration and balance of chemicals in the bath must be meticulously managed. The right composition ensures proper copper ion distribution and adherence to the metal. Regular monitoring and adjustment of the bath’s pH and chemical levels are necessary to maintain its effectiveness. It’s like being a chef in a kitchen, where precision and balance in ingredients make the perfect recipe.
#3 Current Density and Temperature
Control over the electric current and bath temperature is essential. These factors directly influence the rate of deposition and the quality of the copper layer. Too high a current density can lead to rough and uneven deposits, while too low a current density may result in slow plating. Similarly, the correct temperature needs to be maintained for the bath to ensure a smooth plating process.
#4 Plating Time
The duration of the electroplating process affects the thickness and uniformity of the copper layer. It’s important to optimize the time for each specific application. Longer plating times can produce thicker coatings, but may also increase the risk of defects. For instance, in precision electronics, shorter plating times are often used to achieve a fine, uniform layer essential for optimal electrical conductivity.
#5 Post-Plating Treatment
Post-plating processes, such as rinsing, drying, and polishing, are crucial for the final appearance and quality of the product. Proper rinsing removes any residual chemicals, preventing corrosion or staining. Drying is essential to prevent water spots, while polishing enhances the aesthetic appeal of the plated item. These steps are vital to ensure the plated item meets both functional and visual standards.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the intricacies and applications of copper electroplating, offering valuable insights for businesses and professionals in the metal fabrication industry. This knowledge can empower you to make informed decisions and enhance the quality of your metal products.
If you’re looking to apply these techniques to your projects or need expert advice, Zemetal is here to assist. Contact us to start your journey towards improved metal fabrication solutions.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








