Why is chrome and plating a game-changer in the metal fabrication industry? It’s not just about looks; it’s about longevity and quality.
With years of experience in metal fabrication, our insights offer valuable knowledge for businesses seeking durable and cost-effective solutions.
Chrome and plating don’t just add a shiny finish; they protect and enhance the metal’s durability. This technique is transforming how we approach long-term metal protection and aesthetics in various industries.
Discover the intricate processes, benefits, and applications of chrome plating and electroplating, and how they can elevate business.
Keep reading to learn more!
1. Defining Chrome Plating and Electroplating
Chrome plating is a process where a thin layer of chrome is applied to a metal object, primarily for enhancing its surface properties. This technique improves the metal’s corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, and overall aesthetic appeal. The result is a shiny, reflective surface that’s both durable and attractive. Chrome plating really transforms ordinary metal into something special.
Electroplating, a broader term, involves coating a metal object with a layer of another metal using an electrical current. This process is integral to various industries, enhancing properties like corrosion resistance and appearance. According to Future Market Insights, the electroplating market is expected to grow from US$ 20 billion in 2023 to over US$ 30 billion by 2033, advancing at a 4.1% CAGR.
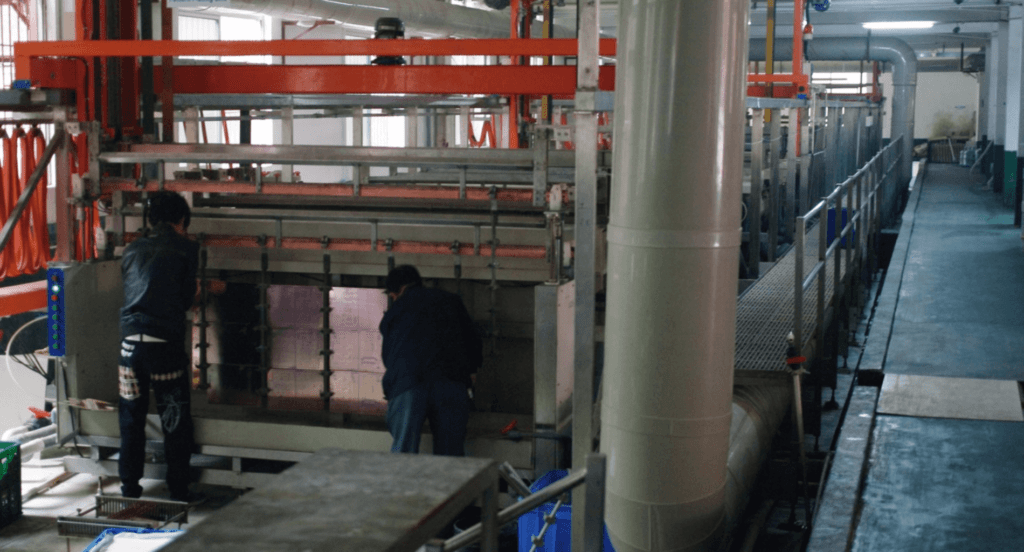

2. Benefits of Chrome Plating and Electroplating
After exploring the basics of chrome plating and electroplating, it’s clear how these processes enhance metal objects. Below are the key benefits of chrome plating and electroplating:
Increased Durability
Chrome plating and electroplating create a barrier that protects metals from corrosion, wear, and tear, significantly extending their service life. This process is particularly beneficial for outdoor metal furniture, offering protection against weather elements. This makes them especially valuable in automotive, aerospace, and other industries where durability is crucial.
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
The shiny, mirror-like finish achieved through chrome plating gives products a visually appealing, high-quality appearance, which is a key selling point in consumer goods. For instance, chrome-plated car rims or kitchen faucets stand out for their sleek and modern look. Electroplating allows for a variety of finishes, enabling customization to suit different styles and preferences.
Improved Surface Properties
These processes can be tailored to enhance specific surface properties like electrical conductivity or to reduce friction, which is essential in electronic and mechanical parts. They provide an added layer of functionality to the metal surfaces, meeting diverse industrial needs. It’s fascinating how a thin coating can significantly boost a product’s performance and versatility.
Eco-Friendly Options
Recent advancements have led to more sustainable methods in chrome and electroplating, promoting eco-friendly manufacturing practices. These innovations include the use of non-toxic chemicals and recycling of materials, making the process safer for both the environment and workers. This shift is crucial for industries aiming to reduce their environmental footprint while maintaining high-quality metal finishes.
Cost-Effective Manufacturing
Electroplating is a strategic method to apply precious metals like gold and silver economically, providing high-end results without the high-end price tag. This technique is particularly beneficial for producing decorative items and jewelry, where the appearance of expensive materials is desired without the associated costs. This approach allows manufacturers to produce luxury-quality items at more affordable prices.
3. Materials and Equipment Used in Chrome Plating and Electroplating
Following the benefits, it’s important to understand the materials and equipment that make chrome plating and electroplating possible. Below are the key materials and equipment used in chrome plating and electroplating:
Plating Tanks
Plating tanks, typically made of materials resistant to chemicals like stainless steel or fiberglass, are used to hold the plating solution, and their design is crucial for ensuring uniform coating of the items. Depending on the operation’s scale and item size, these tanks can range from small benchtop units to large industrial vats. The tank is where the magic happens.
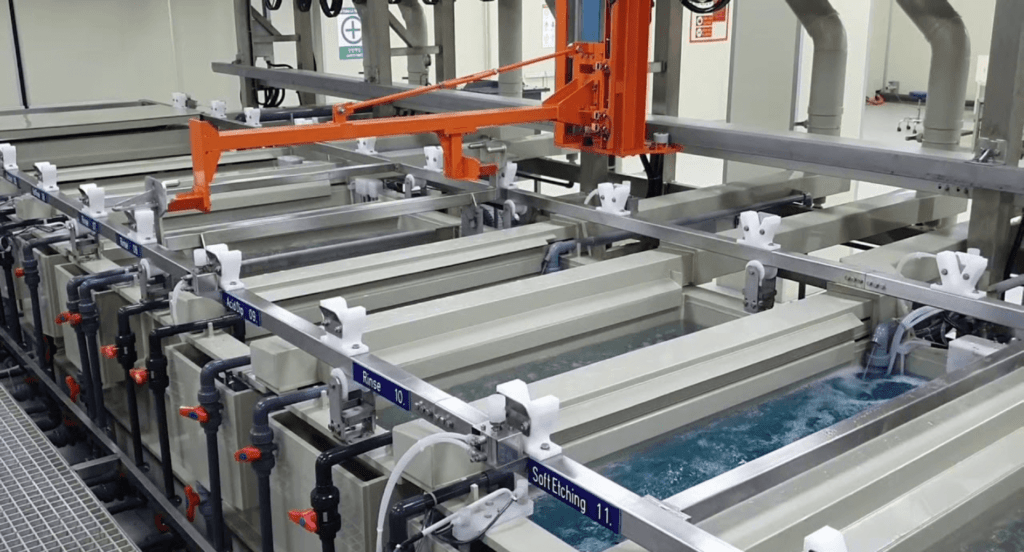
Electrical Power Supplies
Electroplating requires a stable and controllable electrical power supply to facilitate the deposition of metal ions onto the substrate. The precision in controlling the power supply’s voltage and current is essential for achieving the desired plating thickness and uniformity. It’s amazing how a precise burst of electricity can transform a metal’s surface so dramatically.
Anodes and Cathodes
Anodes, often made of the metal being plated, dissolve in the solution and deposit onto the cathode, which is the item being plated. This electrochemical reaction is key, and the quality of the anodes directly affects the finish of the plated item. Regular monitoring and replacement of anodes ensure consistent quality in the plating process.
Chemical Solutions and Additives
Specific chemicals are used for different plating processes; for chrome plating, a chromic acid solution is essential, while other metals require different solutions. Additives in these solutions can control various aspects like brightness, thickness, and plating speed. The precise formulation of these solutions is critical for achieving the specific properties desired in the final plated product.

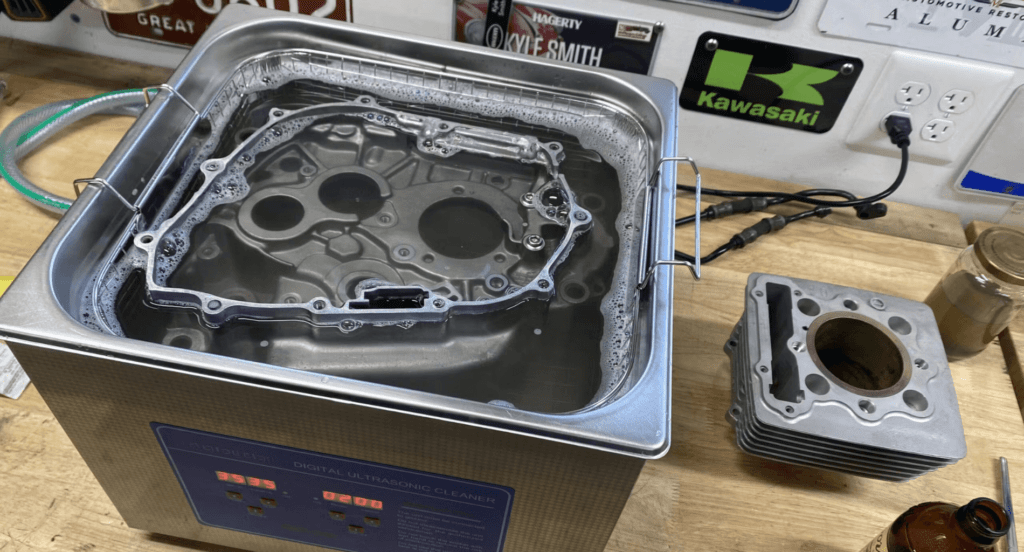
Rinsing and Cleaning Equipment
Proper cleaning and rinsing of the items before and after plating are crucial for ensuring a high-quality finish and preventing defects. This equipment, including ultrasonic cleaners and rinse tanks, is essential for removing any contaminants that might affect the plating quality. Zemetal’s advanced cleaning systems exemplify this, ensuring that each item reaches the plating stage in pristine condition.

4. Cost Factors in Chrome Plating and Electroplating
After understanding the materials and equipment involved, it’s crucial to consider the cost factors that impact chrome plating and electroplating. Below are the key cost factors in chrome plating and electroplating:
Equipment and Maintenance
The initial investment in plating equipment can range from $50,000 to $500,000, with ongoing maintenance costs varying based on the type and scale of the operation. Regular maintenance and equipment replacement can significantly raise long-term costs, sometimes into the tens of thousands. Maintenance and repair frequency, crucial to operational costs, can add an additional 5-10% to the initial investment annually.
Labor Expenses
Labor costs for skilled service personnel in the plating and maintenance process vary, with hourly rates between $15 to $30 or more based on expertise. Training and certification for complex tasks can significantly raise labor expenses, potentially boosting annual costs by 10-20%. Ongoing training for technological updates also notably impacts these costs.
5. Real-world Applications of Chrome and Electroplating
After considering the cost factors, it’s enlightening to look at how chrome and electroplating are applied in real-world scenarios. Below are the real-world applications of chrome and electroplating:
Automotive Industry
Chrome plating is widely used in the automotive industry for both functional and decorative purposes. Components like bumpers, rims, and engine parts are commonly chrome-plated for enhanced durability and aesthetic appeal. In addition, interior features such as trim and dials are often chrome-plated for a stylish finish. Shiny, durable car parts are a hallmark of quality.

Electronics and Electrical Components
Electroplating is crucial in the electronics industry for improving conductivity and preventing corrosion in components like circuit boards and connectors. It’s also used in plating contacts and switches, ensuring optimal electrical performance. For example, smartphones and computers often have electroplated components to enhance their performance and lifespan.
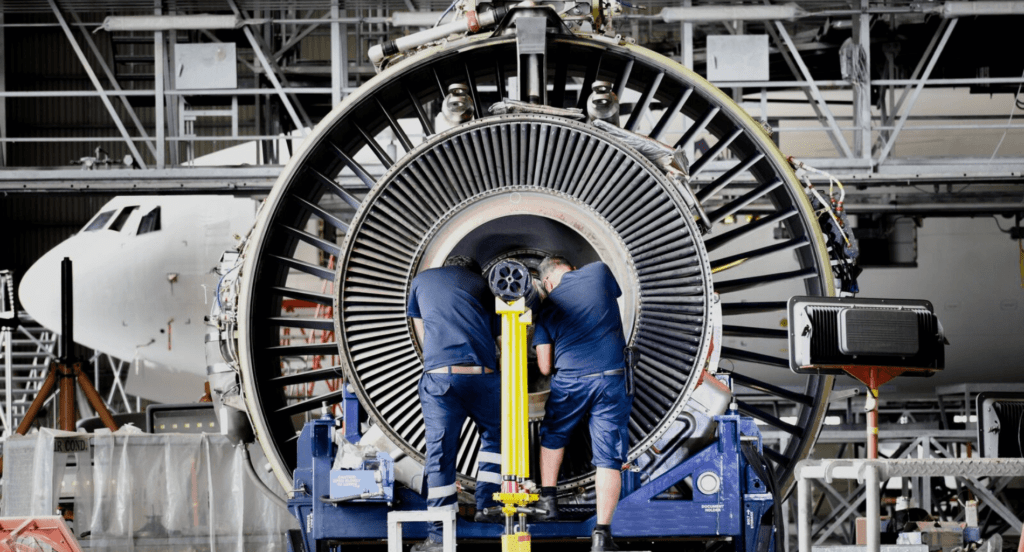
Aerospace and Aviation
In the aerospace sector, electroplating is used to protect components from extreme environmental conditions and reduce wear and tear. It’s particularly important for parts that endure high stress and temperature fluctuations, like turbine blades and cockpit instruments. This application is critical for ensuring the safety and efficiency of aircraft.
Jewelry and Fashion Accessories
Electroplating with precious metals like gold and silver is common in the jewelry industry, providing a cost-effective way to produce luxurious-looking items. This technique is also used to apply protective coatings to prevent tarnishing, as seen in high-end watches and designer jewelry. It also offers protection and longevity to these fashion pieces.

Medical Devices
Chrome and electroplating techniques are employed in medical devices for their anti-corrosive properties and biocompatibility. This ensures that surgical tools and implants maintain their integrity and safe interaction with the human body. This application is vital for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical instruments and implants.
6. Comparative Analysis: Chrome Plating vs Electroplating
After exploring the real-world applications, it’s essential to delve into a comparative analysis of chrome plating versus electroplating. Below are the key points in the comparative analysis of chrome plating vs electroplating:
Process and Technique Differences
Chrome plating is a specific type of electroplating focused on using chromium, while electroplating can involve various metals like nickel, copper, or gold. Chrome plating usually requires several layers for optimum finish, whereas other electroplating methods might need fewer layers depending on the desired outcome. Each method has its unique approach and requirements.
Material Suitability and Applications
Chrome plating is often used for automotive and decorative applications due to its high shine and resistance to tarnish. In contrast, electroplating can be tailored for different materials and purposes, like improving electrical conductivity in electronics or corrosion resistance in aerospace components. Silver plating is preferred in electrical contacts due to its high conductivity.
Cost Implications
The cost of chrome plating can be higher due to the specific chemicals and multiple layering processes involved. Electroplating costs vary widely based on the metal used; gold plating tends to be more expensive than nickel plating, but the long-term benefits of the chosen metal can often offset the initial costs. Project size and item complexity significantly impact the total cost of plating.
Durability and Longevity
Chrome plating typically offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for items exposed to harsh conditions. Electroplating, depending on the metal used, can provide varying levels of durability and is often selected based on the specific requirements of the application. Zinc plating is commonly used for its excellent corrosion resistance in outdoor environments.
7. Environmental Concerns in Chrome Plating and Electroplating
Following the comparative analysis, it’s crucial to address the environmental concerns associated with chrome plating and electroplating. Below are the environmental concerns in chrome plating and electroplating:
Hazardous Chemicals and Waste
Chrome plating often involves toxic chemicals like hexavalent chromium, which is harmful to both humans and the environment. Proper disposal and treatment of waste products are essential to prevent contamination of soil and water. Additionally, the use of alternative, less harmful chemicals is being explored to reduce environmental impact.

Air Quality Issues
The plating process can release harmful fumes and particulates into the air, affecting air quality. Effective ventilation systems and air purification measures are vital to minimize these emissions. Implementing advanced filtration technologies can significantly reduce the release of these harmful substances. Breathing clean air is just as important as producing quality metal finishes.
Water Usage and Contamination
Both chrome plating and electroplating require significant amounts of water, leading to concerns about both usage and potential contamination. Recycling and treating water before disposal is key to reducing environmental impact. The introduction of water-efficient technologies can also help in reducing overall water consumption. Regular water testing ensures compliance with environmental standards.
Energy Consumption
The electroplating process is energy-intensive, contributing to larger carbon footprints. Adopting energy-efficient practices and equipment can help mitigate this concern. The use of renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, is being explored to further reduce the environmental impact of these processes. Zemetal is actively incorporating these sustainable energy solutions into their operations.
8. Future Trends in Plating Technologies
Following the discussion on environmental concerns, it’s intriguing to look at the future trends in plating technologies. Below are the future trends in plating technologies:
Greener Plating Methods
The industry is moving towards more environmentally friendly plating processes, reducing the use of toxic chemicals and improving waste management. Advances in green chemistry are leading to the development of safer alternatives to traditional plating solutions. These methods not only protect the environment but also improve worker safety.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are becoming increasingly prevalent, enhancing precision and efficiency in plating operations. These technologies reduce human error, increase throughput, and can lead to more consistent quality in the plating process. Automation also allows for better scalability of operations, accommodating larger production volumes with greater ease.
Nanotechnology in Plating
Nanotechnology is set to revolutionize the plating industry with the ability to create ultra-thin, highly durable coatings. This technology offers new possibilities in terms of material properties and applications, potentially opening up new markets. Nanocoatings can provide unprecedented levels of protection against corrosion and wear. They enable smart surfaces with self-cleaning and anti-microbial features.
The table below showcases how nanotechnology is transforming the plating industry through innovative nanocoatings, enhancing durability, protection, and functionality of surfaces.
| Nanocoating Feature | Benefit | Potential Applications |
| Ultra-thin layers | Improved material properties | Electronics, aerospace |
| High durability | Extended lifespan of products | Automotive, construction |
| Corrosion protection | Enhanced resistance to environmental damage | Marine, infrastructure |
| Wear resistance | Reduced maintenance and repair costs | Machinery, tools |
| Smart surfaces | Self-cleaning, anti-microbial properties | Healthcare, consumer products |
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the intricate world of chrome plating and electroplating, highlighting their benefits, processes, and environmental considerations. It’s clear how vital these technologies are in various industries, enhancing product quality and sustainability.
For expert guidance or to explore how Zemetal’s plating solutions can elevate your business, reach out to us. Our team is ready to assist you – contact us to start your journey in advanced plating technologies.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








