Most businesses in the metal industry were asking, “How to ensure metal products resist corrosion and maintain aesthetic appeal?” The answer often lies in alkaline zinc plating, an important process in the domain of metal finishing.
With extensive experience in the field of metal finishing and a deep understanding of alkaline zinc plating, I bring insights that are both practical and cutting-edge.
Alkaline zinc plating is more than just a protective coat; it’s a modern process that balances chemical complexity with environmental consciousness, ensuring thelongevity and performance of metal products.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll dive deep into the ideas of alkaline zinc plating, exploring its benefits, applications, and the latest technological advancements that are shaping the industry.
So keep reading to learn more!
1. Fundamentals of Alkaline Zinc Plating
Alkaline zinc plating is a process where a layer of zinc is electrochemically bonded to the surface of metal components. This method utilizes an alkaline-based electrolyte, which is a stark contrast to the more acidic solutions used in other plating techniques. The choice of an alkaline medium offers distinct advantages, including a more uniform distribution of the zinc coating, even on complex geometries.
This uniformity is crucial for parts with complex shapes or deep recesses, where consistent coverage is essential. Furthermore, the alkaline environment in the plating bath enhances the throwing power of the process. This term refers to the ability of the plating solution to deposit zinc efficiently over the entire surface of the part, including hard-to-reach areas.
The result is a comprehensive protective layer that significantly enhances the durability and corrosion resistance of the base metal. Such thorough coverage is important for components used in harsh environments or those requiring a prolonged lifespan. This process not only extends the life of metal parts but also contributes to their aesthetic appeal, adding value to the final product.
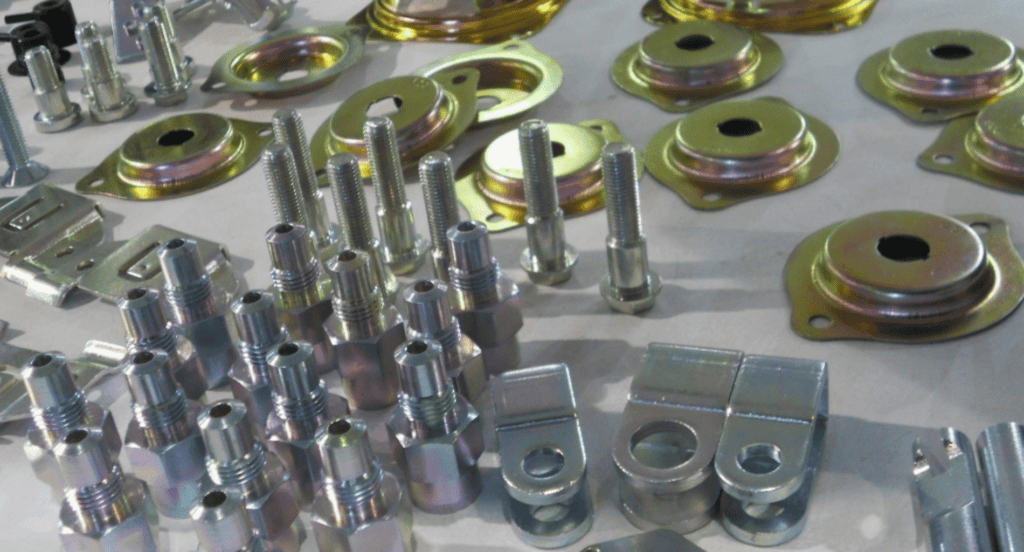
2. Benefits of Alkaline Zinc Plating
After understanding the fundamental process of alkaline zinc plating, it’s important to recognize its key benefits. Here are the primary advantages:
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Alkaline zinc plating provides a formidable barrier against corrosion. The zinc layer acts sacrificially, corroding before the underlying metal, thus significantly prolonging the life of the base material. This makes it an ideal choice for components exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
- Uniform Coating Distribution: The alkaline nature of the solution ensures a uniform and consistent zinc coating, even on parts with complex shapes and deep recesses. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining the integrity and appearance of the coated components.
- Improved Throwing Power: The process exhibits excellent throwing power, meaning it can efficiently coat hard-to-reach areas and surfaces. This attribute ensures comprehensive coverage and protection, which is vital for complex parts.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Beyond functionality, alkaline zinc plating enhances the visual appeal of metal parts. It provides a bright, clean finish that can be further enhanced with various passivation processes, making it suitable for visible components in consumer products.
- Environmental Friendliness: Compared to other plating methods, alkaline zinc plating often involves fewer toxic substances and can be managed to minimize environmental impact. This aspect aligns well with the increasing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly industrial practices.
3. Step-by-Step Process of Alkaline Zinc Plating
Having explored the significant benefits of alkaline zinc plating, it’s essential to understand the step-by-step process that ensures these advantages. Below are the key stages involved in alkaline zinc plating:
Step#1 Surface Preparation
The first and perhaps most crucial step is surface preparation. The metal parts are thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, oil, or other contaminants. This stage determines the quality of the final finish; a well-prepared surface ensures better adhesion and a more uniform coating. Typically, this involves degreasing, pickling, and sometimes abrasive blasting, depending on the part’s condition.
Step#2 Electrolyte Bath
Once the surface is prepared, the parts are submerged in an alkaline electrolyte solution. This solution contains zinc ions, along with other chemicals to facilitate the plating process. It’s crucial to maintain the right composition and temperature of the bath to ensure optimal plating quality. Zemetal services carefully control these parameters to achieve consistent and high-quality zinc deposition.
Step#3 Zinc Deposition
In this stage, an electric current is applied, causing the zinc ions in the solution to adhere to the metal parts. The thickness of the zinc layer can be controlled by adjusting the duration and intensity of the current. I find this part of the process fascinating, as it’s where the actual transformation happens, turning a bare metal into a corrosion-resistant, aesthetically pleasing component.
Step#4 Rinsing and Drying
Following the zinc deposition, the parts undergo a critical rinsing process. This step is vital to ensure that no remnants of the electrolyte affect the quality of the zinc coating. In practice, parts are usually immersed in a series of rinse tanks, often containing deionized or distilled water, to cleanse any residual chemicals thoroughly. For instance, in automotive or aerospace components, this step is thoroughly monitored.
Step#5 Post-Treatment
The final stage in the alkaline zinc plating process involves various post-treatment options, each serving a specific purpose based on the application of the plated part. Common post-treatment processes include passivation and sealing. Passivation involves applying a thin protective coating, often a chromate conversion coating layer, to enhance the corrosion resistance of zinc.
4. Applications of Alkaline Zinc Plating in Industry
Moving from the detailed process to practical applications, alkaline zinc plating finds extensive use across various industries. Below are some of the key sectors where this process plays an essential role:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, alkaline zinc plating is extensively used for coating components that require high corrosion resistance and durability. Parts like fasteners, brackets, and other under-the-hood components are commonly treated with this process. This plating ensures that these parts can withstand the harsh conditions they are exposed to, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to chemicals on the road.
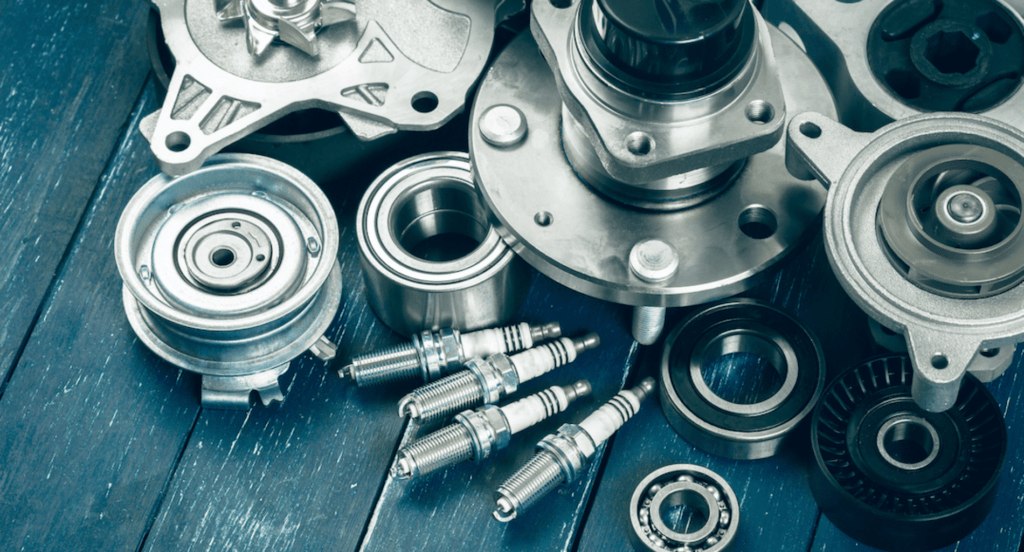
Construction and Infrastructure
Alkaline zinc plating is crucial in the construction and infrastructure industry, especially for metal components used in outdoor settings. It’s applied to hardware like bolts, nuts, and steel frames to protect them from the elements. The zinc coating provides a long-lasting barrier against rust and degradation, which is essential for the longevity and safety of buildings and structures.

Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, where components are often miniaturized and intricate, the uniform coating capability of alkaline zinc plating is particularly beneficial. It’s used for small metal parts within electronic devices, providing not just corrosion resistance but also improved electrical conductivity, which is crucial for consistent performance.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry utilizes alkaline zinc plating for various components, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Here, the process is applied to parts that require a lightweight yet durable coating to withstand extreme environmental conditions. For example, certain connectors and fasteners used in aircraft are zinc-plated to ensure they remain functional and safe over long periods, despite exposure to high altitudes.
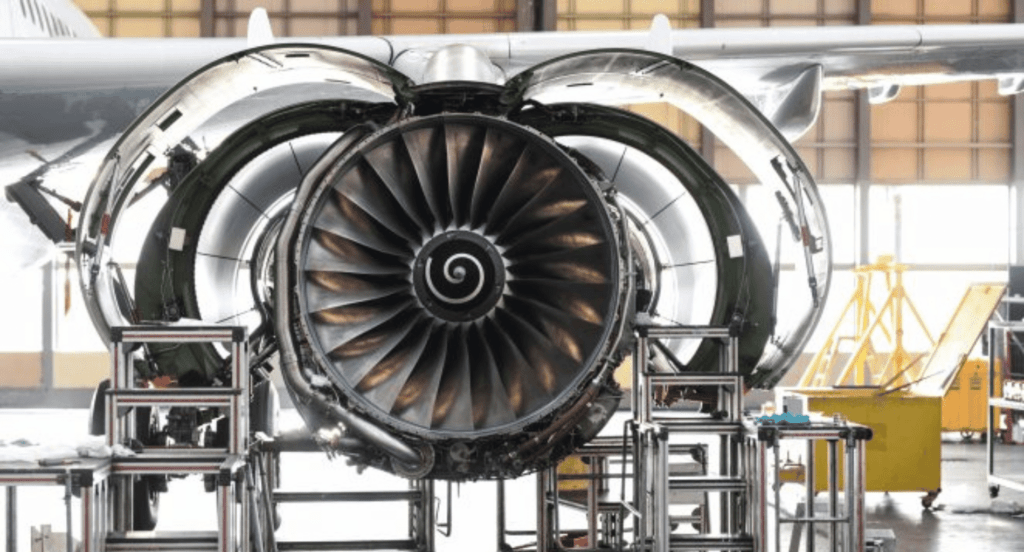
5. Quality Control and Testing in Alkaline Zinc Plating
As we explore the wide range of applications for alkaline zinc plating, it becomes clear that maintaining high quality and consistency is essential. See the following sections for an in-depth look at these practices:
Inspection and Process Control
Quality control in alkaline zinc plating begins with stringent inspection and process control measures. Parameters like bath composition, temperature, and current density are continuously measured and adjusted to maintain optimal conditions. Zemetal’s services employ comprehensive process control systems to ensure that each batch of plated components meets the highest quality standards.
Thickness and Adhesion Testing
After plating, the thickness and adhesion of the zinc coating are key quality indicators. Thickness is typically measured using electronic gauges that provide precise readings, ensuring the coating is within specified limits. This is crucial, as the thickness directly correlates with the corrosion resistance and durability of the coating. Adhesion testing ensures that the zinc layer firmly adheres to the base metal.
Corrosion Resistance Testing
To verify the effectiveness of the zinc coating, corrosion resistance testing is conducted. This involves exposing the plated parts to controlled corrosive environments, such as salt spray or humidity chambers, for predetermined periods. I believe the performance of the coating is then assessed based on the degree of corrosion that occurs during these tests.
6. Common Issues Faced During the Plating Process
While alkaline zinc plating is a robust and effective method, like any industrial process, it is not without its challenges. Here are the most common problems encountered during the plating process:
Inadequate Cleaning
One of the primary issues in alkaline zinc plating is inadequate cleaning of the metal surface before plating. Residues such as oils, greases, or oxidation can prevent the even deposition of zinc, leading to poor adhesion and coverage. This can result in a patchy appearance and compromised corrosion resistance. For example, a batch of fasteners with inadequate pre-cleaning may show uneven zinc distribution.
Irregular Coating Thickness
Achieving a uniform coating thickness can be challenging. Variations can occur due to inconsistencies in the electroplating bath, uneven electrical currents, or improper part positioning. Irregular thickness not only affects visual appeal but also impacts functional attributes like corrosion resistance. Consistent monitoring and adjustment of the plating parameters are essential to avoid this issue.
Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement is a concern, particularly for high-strength steel. During the plating process, hydrogen atoms can be absorbed into the metal, leading to brittleness and potential failure under stress. To prevent this, parts may require a post-plate baking process to release trapped hydrogen. This issue underscores the importance of understanding the material properties and selecting appropriate post-treatment methods.
Disposal and Environmental Impact
Environmental impact and waste disposal are significant challenges in the plating industry. The chemicals used in the process, if not managed correctly, can have damaging effects on the environment. Implementing sustainable practices, such as recycling and treating waste products, is crucial. Regulatory compliance and adopting eco-friendly alternatives help in reducing the environmental footprint of the plating process.
This table highlights the challenges and solutions in managing environmental impact and waste disposal in the plating industry, underscoring the importance of sustainable practices.
| Challenge/Solution | Description | Impact on Environmental Sustainability |
| Chemical Waste Management | Proper handling and disposal of hazardous chemicals | Reduces potential environmental harm |
| Recycling of Waste Products | Reusing materials to minimize waste | Promotes resource conservation |
| Waste Treatment Facilities | Treating waste to remove harmful substances | Prevents contamination of ecosystems |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to environmental laws and guidelines | Ensures industry accountability |
| Adoption of Eco-Friendly Alternatives | Using less harmful substances in plating processes | Decreases ecological footprint |
7. Emerging Trends in Alkaline Zinc Plating Technology
Recognizing and addressing common issues in the alkaline zinc plating process is important for continuous improvement. Let’s explore the cutting-edge advancements in this field:
Automation and Process Control
The integration of automation and advanced process control technologies is revolutionizing alkaline zinc plating. Automated systems allow for precise control of plating parameters, leading to higher consistency and quality in the final product. Moreover, real-time monitoring and data analytics are being used to optimize processes, reduce waste, and enhance overall efficiency.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is finding its way into zinc plating, offering new possibilities for coating performance. Scientists are developing zinc coatings with enhanced properties. Industrialized nations spend 5% of GNP (gross national product) on corrosion protection, replacement of corroded parts, maintenance work, and environmental protections according to MSRI.
Advanced Post-Treatment Techniques
Finally, advancements in post-treatment techniques are providing additional value to alkaline zinc-plated parts. These include new types of sealants and passivation processes that enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Innovative treatments can also impart additional functional properties, like improved electrical conductivity or reduced friction, broadening the application scope of zinc-plated parts.
Conclusion
Knowing alkaline zinc plating, from its fundamentals to emerging trends, equips businesses with the knowledge to enhance their metal finishing practices. This guide serves as a valuable resource for understanding and going through the details of this essential industrial process.
If you’re seeking expertise in alkaline zinc plating, Zemetal offers state-of-the-art services tailored to all needs. Discover how our solutions can elevate your projects by contacting us today.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








