In the field of sheet metal fabrication, how are the latest advancements in laser cutting technology transforming business capabilities and design? This sector is experiencing a rapid evolution, enhancing precision and efficiency at a fast pace.
As an expert in sheet metal laser cutting design, I bring a wealth of experience and insight into these technological innovations.
Sheet metallaser cutting design is not just about cutting metal; it’s an art that matches innovation, precision, and functionality.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll delve into the cutting-edge techniques and emerging trends that are setting new standards in the industry.
So keep reading to learn more.
1. Understanding the Technology Behind Laser Cutting
Laser cutting stands as a cornerstone in modern sheet metal fabrication, distinguished by its precision and versatility. At its core, this technology utilizes a high-powered laser beam, guided by computer numerical control (CNC), to cut and shape metal sheets with remarkable accuracy. The laser beam, focused to a fine point, melts, burns, or vaporizes the metal in a controlled and precise manner.
This process is highly efficient, reducing material waste and offering unparalleled precision. Moreover, the adaptability of laser cutting technology caters to a wide range of metals, including steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. Its ability to produce complex shapes and fine details without the need for additional tooling makes it an invaluable tool in the fabrication industry.
By integrating advanced software, laser cutting machines can quickly interpret design files, translating intricate patterns into precise cuts and engravings. This seamless integration of technology and design capability is what sets laser cutting apart, enabling businesses to push the boundaries of metal fabrication.

2. Advantages of Laser Cutting in Metal Design
Having understood the technology behind laser cutting, it’s evident why this method is important in metal design. It’s not just the precision and versatility that make it stand out. Now, here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Precision and Accuracy: Laser cutting offers unmatched precision, enabling the creation of intricate designs and tight tolerances that are impossible with traditional cutting methods. This accuracy is crucial for complex components in various industries, ensuring consistency and quality.
- Increased Efficiency and Speed: Compared to conventional cutting techniques, laser cutting significantly reduces processing time. It allows for rapid production without sacrificing quality, making it ideal for meeting tight deadlines and high-volume demands.
- Flexibility in Design: The adaptability of laser cutting extends to its ability to handle multiple designs and shapes without the need for changing tools. This flexibility enables designers to experiment with complex patterns and shapes, fostering innovation in metal design.
- Compatibility with Various Materials: This technology is versatile enough to cut a wide range of metals, from thin sheets to thicker plates. This compatibility makes laser cutting a universally preferred choice in the fabrication industry, suitable for diverse project requirements.
3. Design Considerations for Laser Cutting
Following the advantages of laser cutting in metal design, it’s crucial to delve into specific design considerations that ensure optimal results. Let’s see the essential aspects to consider:
Material Selection
The choice of material greatly impacts the outcome of a laser cutting project. While laser cutters can work with a variety of materials, each reacts differently to the laser beam. For instance, metals like aluminum and copper, known for their high reflectivity and thermal conductivity, require more laser power. Designers must understand material properties, such as thickness, reflectivity, and heat resistance.
Kerf Precision
Kerf refers to the width of the material removed during the cutting process. In laser cutting, the kerf is typically small, but it varies depending on the material thickness and the type of laser used. Designers must account for the kerf in their designs when parts need to fit together precisely. For example, in designing a jigsaw puzzle, the kerf size must be considered to ensure pieces fit together seamlessly.
Complex Geometries and Tolerances
One of the strengths of laser cutting is its ability to produce complex shapes and fine details. However, designers must balance complexity with practicality. Extremely intricate designs may be difficult to cut accurately or may require slower cutting speeds, impacting efficiency. Additionally, designers must understand the tolerance levels that laser cutting can achieve and design within these parameters.
This table illustrates the balance between complexity and practicality in laser cutting, focusing on the trade-offs and considerations when dealing with complex geometries and tolerances.
| Aspect | Consideration | Impact on Laser Cutting Process |
| Design Complexity | Feasibility and accuracy of intricate cuts | May require slower speeds for precision |
| Cutting Speed | Speed versus detail accuracy | Faster speeds may reduce detail quality |
| Tolerance Levels | Precision achievable by laser cutting | Dictates the limit of design intricacy |
| Material Considerations | Suitability of materials for fine details | Some materials may not support complex cuts |
| Cost Implications | Higher complexity can increase costs | Needs balancing with budget constraints |
Nesting
Nesting refers to the efficient layout of designs on a material sheet to minimize waste. Effective nesting is crucial for cost-effectiveness and sustainability. By strategically arranging parts to be cut, designers can maximize material usage and reduce scrap. This consideration is not only economically beneficial but also aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
4. Advanced Techniques in Laser Cutting Design
Recognizing the design considerations for laser cutting sets the stage for exploring advanced techniques that can further enhance the process. Here are some of the most innovative methods currently in use:
3D Laser Cutting
Moving beyond traditional flat-sheet cutting, 3D laser cutting opens up a realm of possibilities for complex shapes and structures. This technique involves manipulating the laser head along three axes, allowing for intricate cuts on curved surfaces, tubes, and profiles. It’s particularly useful for automotive and aerospace components, where precision and complexity are paramount.

Laser Engraving and Etching
Laser engraving and etching are techniques used to create detailed markings on metal surfaces without cutting through the material. Engraving involves removing part of the surface to create a design, while etching merely alters the surface’s properties for a visible effect. This is ideal for adding serial numbers, logos, or decorative patterns to metal parts.

Multi-Head Laser Cutting
In multi-head laser cutting, multiple laser heads operate simultaneously on a single machine. This approach significantly increases productivity by allowing for multiple operations or cuts to occur at the same time. It’s particularly effective for large-scale production runs or when identical parts are needed in high volumes. Imagine cutting several identical gears simultaneously, drastically reducing production time.

Rapid Prototyping
Laser cutting is an invaluable tool for rapid prototyping, allowing designers to quickly turn digital models into physical prototypes. This capability is crucial in industries where design iterations and functional testing are frequent. A designer could, for example, rapidly prototype a new component for a custom machinery project, test it, and refine the design in a fraction of the time traditional methods would take.
5. Software and Tools for Designing Laser-Cut Sheet Metal
With the exploration of advanced techniques in laser cutting design, it becomes clear that the right software and tools are fundamental to utilizing these capabilities fully. Let’s see the key types of software and tools:
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) Software
CAD software is the cornerstone of laser-cut design, allowing designers to create detailed and precise 2D or 3D models of their intended projects. These programs provide a platform to conceptualize and visualize complex designs before they’re brought to life. CAD tools often include features like material simulation and tolerance testing, which are crucial for ensuring that designs are both practical and feasible.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) Software
CAM software bridges the gap between design and production, converting CAD models into machine-readable instructions for laser cutters. This translation is essential for ensuring that the intricacies of the design are accurately replicated in the cutting process. The global Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) market size was valued at USD 3695.65 Million in 2022 and will reach USD 5930.0 Million in 2028 according to LinkedIn.
Simulation and Prototyping Tools
Simulation tools play a pivotal role in predicting how designs will behave during and after the cutting process. These tools can simulate factors like heat impact, material stress, and bending, allowing designers to make preemptive adjustments. Additionally, rapid prototyping tools enable the quick creation of physical samples from CAD designs, essential for testing and validating design concepts.
6. Innovative Applications in Sheet Metal Design
The advancement of software and tools for designing laser-cut sheet metal has paved the way for a multitude of innovative applications in various industries. Below are the innovative applications transforming the landscape of metal fabrication:
Architectural Elements
In the world of architecture, the application of laser-cut sheet metal has brought a new dimension to building aesthetics and functionality. From complex elements to detailed decorative panels, laser cutting allows architects to create unique, bespoke designs that were once considered impossible. Personally, I find it fascinating how a simple sheet of metal can be transformed into an architectural masterpiece.
Automotive Parts
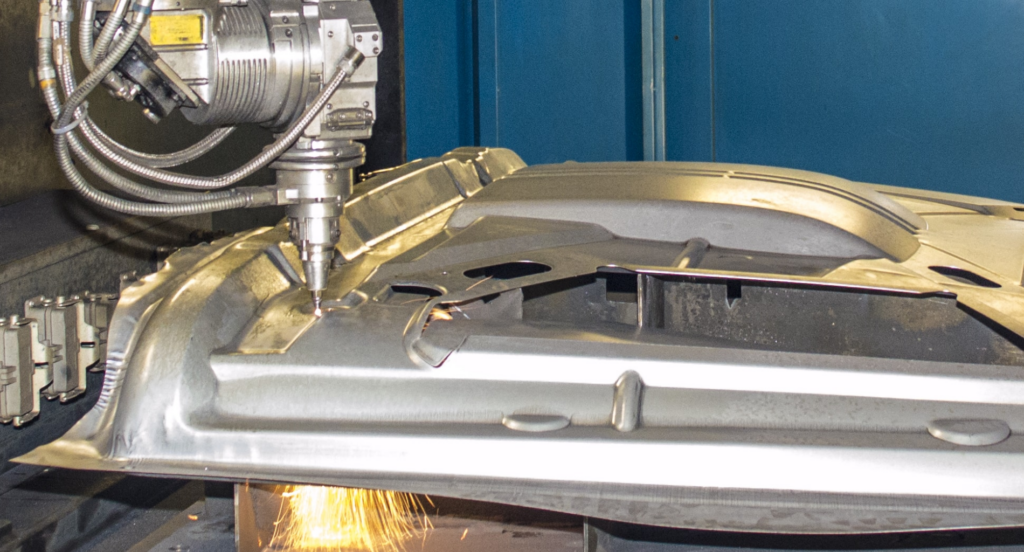
The automotive industry greatly benefits from the precision and efficiency of laser-cut sheet metal. Complex components like brackets, frames, and decorative trim can be produced with high accuracy, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal performance. This technique is particularly valuable in producing lightweight, high-strength parts for modern vehicles. Zemetal offers services in this field that meet strict industry standards.

Medical Devices
Sheet metal design plays a crucial role in the medical device sector. Precision is paramount in this industry, where even a fraction of a millimeter can make a significant difference. Laser cutting allows for the production of intricate components used in surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. It’s personally rewarding to see how these crafted metal parts can directly impact the quality of healthcare.

Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, laser-cut sheet metal is used to create components for devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets. The ability to produce small, precise parts with a high degree of complexity is essential for the miniaturization and functionality of these gadgets. It’s exciting to think that the sleek metal casing of your latest smartphone might have been laser-cut, showcasing the blend of technology and design.
7. 4 Tips for Choosing the Right Laser Cutting Design Service
The innovative applications in sheet metal design underscore the importance of selecting a proficient laser cutting design service. See the following tips to help you choose the right service provider for your needs:
#1 Technical Expertise and Equipment
The first step is to evaluate the technical expertise and equipment of the laser cutting service. A provider with advanced laser cutting machines and a team of skilled professionals can deliver high-precision and quality results. Make sure to opt for brands that are known for their state-of-the-art equipment and experienced personnel, ensuring that even the most complex designs are executed flawlessly.
#2 Reviewing Portfolio and Past Projects
A service provider’s portfolio can give you insight into their capabilities and the types of projects they excel in. Personally, I believe that a diverse portfolio indicates versatility and a breadth of experience. Zemetal is a known provider whose past projects reflect a high standard of quality and creativity, similar to the kind of work each client requires.
#3 Post-Processing Services
Inquire about the range of post-processing services offered. Comprehensive services, including bending, welding, and surface finishing, can be a significant advantage, offering a one-stop solution for your fabrication needs. This not only streamlines the production process but also ensures that the final product is fully finished and ready for use.
#4 Evaluate Cost-Effectiveness
Finally, consider the cost-effectiveness of the services offered. While cost shouldn’t be the only deciding factor, it’s important to ensure that you receive value for your investment. Compare pricing with the quality of services provided, and consider the long-term benefits of working with a provider that meets all your requirements effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, this guide has revealed the complexities of laser cutting in sheet metal design, providing essential insights for informed decision-making. It serves as a valuable resource for businesses seeking to optimize their fabrication processes and achieve superior outcomes.
For those looking to implement these insights, Zemetal offers expert laser cutting services tailored to your unique needs. To explore our services or for any inquiries, kindly contact us.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








