What is sheet metal fabrication? It’s the process of cutting, bending, and assembling flat sheets of metal into specific shapes or components used in various structures and products.
As an Architect, I often get asked about how sheet metal fabrication can be used to create durable and aesthetically pleasing building elements.
Don’t worry, the process is simple to understand and highly versatile.
In this guide, you will learn the basics of sheet metal fabrication, the techniques involved, and how it’s applied in different industries. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how this process can enhance your projects.
Let’s get started!
1. Defining Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is a comprehensive process that involves the transformation of sheets of metal into products or structures through various techniques. This process, central to the manufacturing and construction industries, employs cutting, bending, and assembling methods. It enables the creation of everything from complex components used in machinery to large-scale structural elements.
The versatility of sheet metal fabrication lies in its ability to work with diverse metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass. This flexibility makes it a go-to solution for businesses seeking custom metal solutions, ranging from HVAC components to automotive parts. The process not only caters to functional needs but also allows for aesthetic customization, crucial in sectors like architecture and automotive.
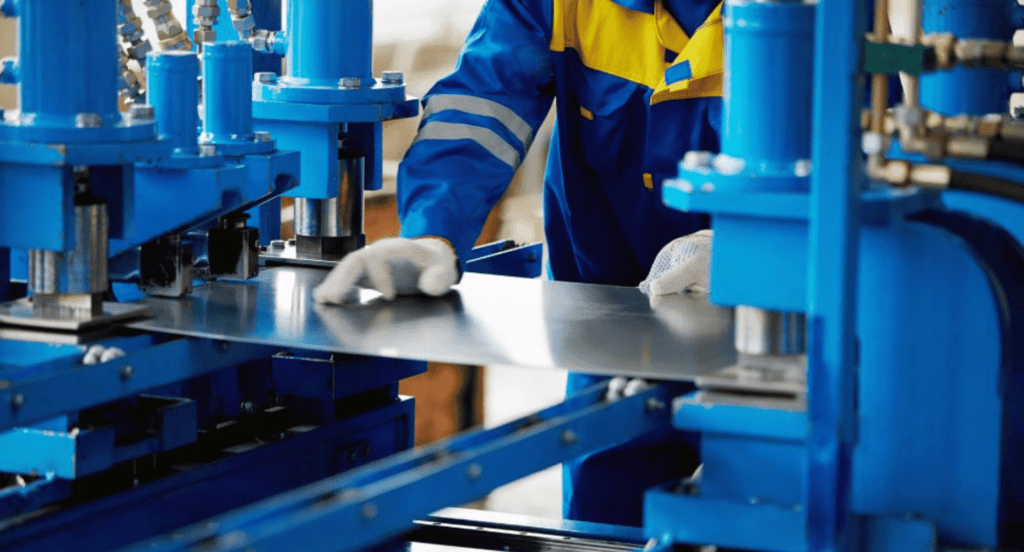

2. Materials Used in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Transitioning from the basic understanding of sheet metal fabrication, it’s crucial to delve into the materials that play a role in this process. Here are the key materials commonly used in sheet metal fabrication:
Aluminum
Aluminum stands out for its lightweight yet strong nature, making it a preferred choice for industries where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and automotive. Its resistance to corrosion and its ability to conduct heat and electricity efficiently add to its versatility. For example, in the automotive industry, aluminum is often used for body panels, enhancing fuel efficiency without compromising on strength.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength and resistance to corrosion and heat. This makes it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as in chemical processing or outdoor infrastructure. Its ability to withstand extreme conditions without deteriorating ensures longevity, a key consideration for businesses investing in long-term assets.
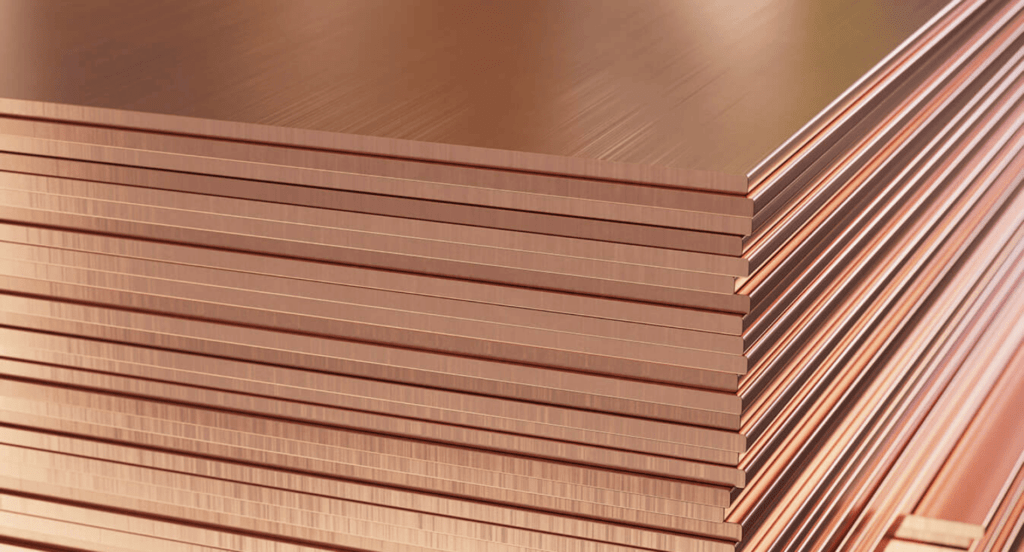
Copper
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, making it indispensable in electrical components. It’s also used for its thermal conductivity in heat exchangers and other heating and cooling applications. Besides its functional attributes, copper’s unique aesthetic appeal is valued in decorative elements and architectural features.

Brass
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, offers a balance between strength and malleability, making it easy to work with. It’s particularly favored for its acoustic properties in musical instruments and its aesthetic appeal in decorative items. In a business setting, brass is often chosen for its professional yet elegant finish in fixtures and fittings.
3. Advanced Fabrication Techniques
Having explored the various materials used in sheet metal fabrication, it’s essential to shift our focus to advanced techniques. Let’s explore the advanced fabrication methods shaping the industry today:
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting stands at the forefront of precision fabrication techniques. It utilizes high-powered lasers to cut metal sheets with remarkable accuracy, creating intricate patterns and detailed shapes that were once considered too complex. This method is highly efficient for mass production, reducing waste and saving time. Its capability to produce precise, clean cuts makes it a popular choice in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting is another advanced technique, using high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to cut through metal. This method is ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures, as it does not generate heat like traditional cutting methods. Zemetal’s services utilize waterjet cutting exemplifies the commitment to preserving material integrity while ensuring precision.
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining transforms fabrication by automating the control of machining tools with a computer. This technology allows for complex shapes and high precision in metal parts. CNC machining is crucial in industries requiring high levels of accuracy, such as in the production of mechanical components and intricate machinery parts.
4. Sheet Metal Fabrication Processes
After examining the advanced techniques in sheet metal fabrication, it’s now time to look at the core processes that bring these techniques to life. Let’s break down the key fabrication processes:
Step#1 Cutting
Cutting is the foundational process in sheet metal fabrication, involving the slicing of large sheets into smaller, usable pieces or specific shapes. Techniques like laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and shearing are employed, each suitable for different materials and thicknesses. This step is critical for ensuring precision in the final dimensions of the product.
Step#2 Bending
Bending is a process where metal sheets are manipulated to form angles and curves. This is typically achieved using press brakes and other bending machinery. The precision and angle of the bend are crucial for the functionality and fit of the final product. Zemetal’s service in this area ensures that each bend meets the exact specifications required for the project.
Step#3 Punching
Punching involves creating holes or cut-outs in the metal sheet. This is done using a punch press, which forcibly creates holes of various shapes and sizes. This process is essential for parts that require assembly, ventilation, or decorative patterns. The accuracy of punching is paramount for the alignment and assembly of parts.
Step#4 Welding
Welding is a critical process in sheet metal fabrication, used to join cut and shaped pieces into a final product. Techniques like TIG, MIG, and spot welding are commonly used, depending on the metal type and the required strength of the joint. Welding not only provides structural integrity but also ensures the durability of the product.
Step#5 Finishing
The finishing process involves treating the surface of the metal to enhance its appearance and resistance to corrosion. Processes like sandblasting, painting, powder coating, and anodizing are used to achieve the desired finish. This step is crucial for both the aesthetic appeal and the longevity of the metal product.
5. Industry Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
From the detailed exploration of the processes involved in sheet metal fabrication, it becomes evident how these techniques are applied across various industries. Here are the primary industry applications:
Construction and Architecture
In the world of construction and architecture, sheet metal fabrication is a key player. It’s used for creating structural elements, roofing, and decorative features. The flexibility of sheet metal makes it ideal for designing unique architectural elements that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. For example, custom metal cladding on buildings not only protects the structure but also provides a modern and distinctive look.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on sheet metal fabrication for producing vehicle components such as body panels, frames, and engine parts. The precision and strength required in automotive parts are a testament to the advanced fabrication techniques used. Sheet metal allows for the production of lightweight yet durable parts, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the vehicle.
Aerospace and Aviation
In aerospace and aviation, the demand for precision and lightweight materials is at its peak. Sheet metal fabrication meets these requirements by producing parts that are crucial for the safety and performance of aircraft. This includes components like fuselage panels, wings, and various internal mechanisms. The strict standards in this industry showcase the high level of skill and technology involved in sheet metal fabrication.
6. Cost Factors in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Understanding the diverse applications of sheet metal fabrication in various industries naturally leads to the question of cost. Let’s see the key factors that determine the cost of sheet metal fabrication:
Material Type and Quality
The type and quality of material used in fabrication are among the primary cost determinants. Different metals, such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, or brass, vary in price due to their availability and inherent properties. High-quality materials that offer enhanced durability or specialized properties, like corrosion resistance, typically come at a higher cost. The choice of material directly impacts the overall project cost.
Complexity of Design and Fabrication Processes
The complexity of the design and the fabrication processes involved also significantly affect the cost. Intricate designs requiring advanced techniques like laser cutting or precision CNC machining often increase the price. Additionally, complex shapes and tight tolerances demand more time and skill, which in turn adds to the cost. The more intricate the design and the more specialized the fabrication process, the higher the cost will be.
Quantity and Scale of Production
The quantity and scale of production play a crucial role in determining cost. Large-scale production typically benefits from economies of scale, where the cost per unit decreases as the quantity increases. However, small, customized orders often carry a higher price per unit due to the setup costs and the need for details. Businesses need to consider the scale of their project and how it will affect the overall cost of fabrication.
7. Safety Practices in Metal Fabrication
As we consider the cost factors in sheet metal fabrication, it’s equally important to focus on safety practices. See the following essential safety practices in metal fabrication:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the first line of defense against potential hazards in a fabrication workshop. This includes safety glasses to protect against flying debris, gloves to handle sharp metal edges, and ear protection in high-noise environments. Regular training and strict enforcement of PPE usage are crucial to prevent accidents and injuries.
Machine Guarding and Maintenance
Proper machine guarding is essential to prevent direct contact with moving parts of fabrication equipment. Guards on machines like press brakes, shears, and punch presses minimize the risk of cuts, amputations, and crushing injuries. Regular maintenance of machinery is equally important. Keeping equipment in optimal condition prevents malfunctions that could lead to accidents.
Safety Protocols
Comprehensive training for all employees is a cornerstone of a safe fabrication environment. This includes training on the proper use of machines, understanding of safety protocols, and emergency response procedures. Safety protocols should be communicated and displayed in the workshop. Regular safety drills and meetings help reinforce safe practices and prepare the workforce for potential emergencies.
The table below highlights key components of comprehensive training for a safe fabrication environment:
| Component | Description |
| Machine Use Training | Instructs employees on the correct operation of machinery to prevent accidents and ensure efficiency. |
| Safety Protocol Education | Educates on established safety guidelines and procedures to minimize risks and hazards in the workshop. |
| Emergency Response Drills | Prepares employees for potential emergencies through simulated scenarios, ensuring quick and effective response to real-life situations. |
| Visual Safety Guides | Utilizes posters and signs in the workshop to continuously remind employees of safety protocols and emergency procedures. |
| Regular Safety Meetings | Conducts periodic discussions and updates on safety practices, allowing for the reinforcement of safe practices and addressing any new concerns or changes. |
8. 3 Tips for Choosing Metal Fabrication Services
After safety practices, another key is selecting the right fabrication service provider. As per LinkedIn, the global Sheet Metal Fabrication Services market is projected to reach US$ 3464.8 million by 2029. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
#1 Consider the Range of Services Offered
A fabricator that offers a comprehensive range of services can be a valuable asset. This includes cutting, bending, welding, and finishing, among others. A service provider with a broad range of capabilities can handle various aspects of your project in-house, offering better control over quality, time, and cost. It simplifies logistics and communication, as dealing with a single entity for multiple services.
#2 Review Cost and Time Efficiency
Cost and time efficiency are important factors in choosing a fabrication service. Obtain detailed quotes from potential fabricators and compare them, considering not only the price but also what is included in the cost. Be wary of unusually low quotes, as they might indicate compromises in quality or hidden costs. Also, discuss project timelines and their ability to meet deadlines.
#3 Evaluate Expertise and Experience
The experience and expertise of a fabrication service are fundamental to the success of your project. Look for a service provider with a proven track record in your specific industry or for your type of project. Experienced fabricators will have a deeper understanding of the challenges and requirements of different projects, ensuring they can deliver high-quality work that meets all specifications.
Conclusion
If you’re finding it difficult to produce customized metal parts with precision, sheet metal fabrication is an efficient and reliable solution. It provides flexibility and strength, making it ideal for a wide range of projects. At Zemetal, we offer expert fabrication services tailored to your exact specifications.
In conclusion, this guide has given you a clear understanding of what sheet metal fabrication is and its importance in various industries. With this knowledge, you can better apply these techniques to improve your projects. Contact us today to learn how Zemetal can assist you with top-tier sheet metal fabrication services.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
For some insightful reads, we’ve curated a list of recommended articles just for you:
Coating Processes
Surface Preparation
- Sandblasting and Powder Coating: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Essential Guide to Blasting and Painting Techniques
- Unveiling the Potential of Blasting and Powder Coating
- Exploring the Power and Precision of Sand and Water Blasting Techniques
- Sandblasting vs. Soda Blasting: A Comparative Guide for Surface Treatment Techniques
Metal Finishing Techniques
- Anodizing vs Electroplating: The Ultimate Battle for Metal Protection
- Anodizing vs Galvanizing: Choosing the Right Metal Finish
- Nickel Plating vs Zinc Plating: The Ultimate Comparison
- Geomet Coating vs. Zinc Plating: Choosing the Right Surface Finish
- The Essential Guide to Chrome Plating and Electroplating Techniques
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








