What if the precision and efficiency of your metal fabrication processes could be enhanced? Look no further than laser cutting and welding.
With years of experience in the industry, our insights offer a valuable perspective on these transformative techniques.
Laser cutting and welding is a standard of precision and efficiency in metal fabrication. These methods have significantly advanced the field, offering unparalleled accuracy and speed compared to traditional methods.
In this article, we will delve into how laser cutting and welding work, their benefits, and the diverse applications they serve in the metal fabrication industry.
Keep reading to discover more about these technologies.
1. The Science Behind Laser Cutting and Welding
Laser cutting and welding harness the power of highly concentrated light beams to manipulate metal with extraordinary precision. In laser cutting, a focused laser beam melts, burns, or vaporizes the material, creating precise cuts and intricate shapes. The laser’s intensity, speed, and heat output are carefully calibrated to suit different metals and thicknesses, ensuring clean cuts and minimal material distortion.
Laser welding, on the other hand, uses a high-energy laser beam to fuse metal pieces together. Unlike traditional welding, laser welding minimizes thermal distortion, preserving the integrity of the material. The precision and control offered by laser welding make it ideal for applications requiring meticulous detail and strength.
2. Advantages of Laser Cutting and Welding
Building on the scientific principles discussed in the previous section, the advantages of laser cutting and welding are numerous and transformative for the metal fabrication industry. Here are four key benefits:
Enhanced Precision and Accuracy
Laser cutting and welding offer unparalleled precision compared to traditional metal fabrication methods. The laser beam’s ability to focus on a minuscule area allows for incredibly detailed cuts and welds. This precision is crucial in industries where even the slightest deviation can compromise the integrity of a product, such as in aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
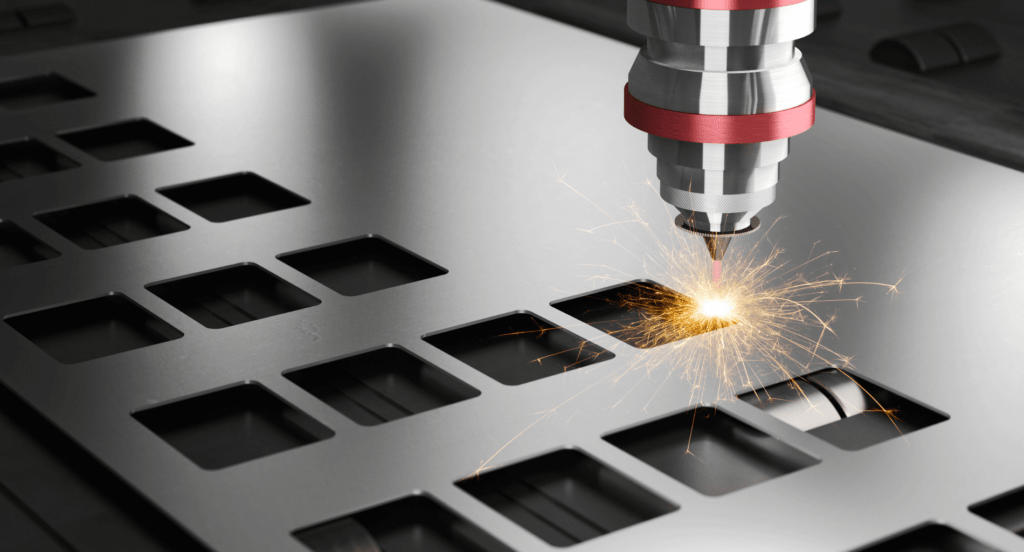
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Laser technologies significantly reduce the time involved in cutting and welding processes. The speed and ease of programmability of laser systems mean that jobs can be completed more quickly and with less manual intervention. This efficiency translates into faster production times and the ability to meet tighter deadlines, providing a substantial competitive advantage.
Versatility and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of laser cutting and welding is their versatility. These processes can be applied to a wide range of materials, including different types of metals and varying thicknesses. At Zemetal, the ability to easily reprogram the laser machines allows for quick shifts between different designs and specifications, making them ideal for custom and diverse projects.
Reduced Material Waste
Laser cutting is known for its ability to maximize material usage, thereby reducing waste. The precision of the laser beam minimizes excess cuts and material usage, which is not only cost-effective but also environmentally friendly. This aspect is particularly appealing to businesses looking to optimize resource efficiency and reduce their ecological footprint.
3. Advanced Techniques and Innovations
Following the exploration of the advantages of laser cutting and welding, it’s clear that these technologies are continuously evolving. Here are some of the most significant developments:
Fiber Laser Technology
Fiber laser technology represents a major leap in laser cutting efficiency and quality. Unlike traditional lasers, fiber lasers use a seed laser and amplify it through special fibers, resulting in a more focused beam that cuts through materials faster and with greater precision. This technology not only enhances performance but also reduces operational costs due to its energy efficiency and lower maintenance requirements.
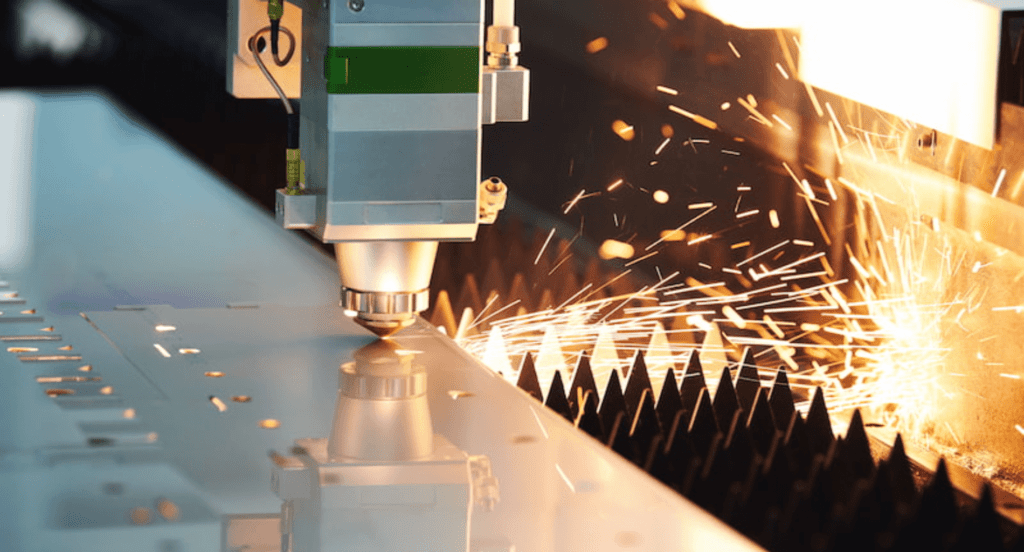

3D Laser Cutting and Welding
3D laser cutting and welding are revolutionary in handling complex shapes and contours. This innovation extends the capabilities of traditional 2D laser cutting, allowing for the precise fabrication of components with intricate geometries. Similarly, 3D laser welding offers enhanced flexibility and precision in joining parts with complex shapes or in hard-to-reach areas.
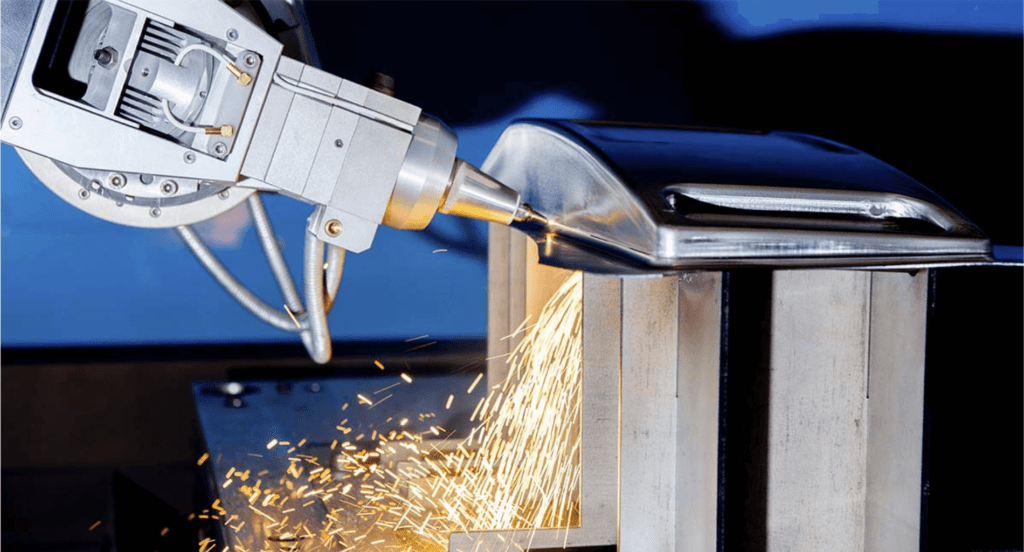

Automation and AI Integration
The integration of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) in laser cutting and welding processes is setting new standards in the industry. Automated systems equipped with AI algorithms can optimize cutting paths, adjust parameters in real-time, and even predict maintenance needs, leading to increased productivity and reduced downtime. This integration paves the way for smarter, more efficient production lines.
4. Applications in Various Industries
The advanced techniques and innovations in laser cutting and welding have opened up a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some key industries where laser cutting and welding are making a significant impact:
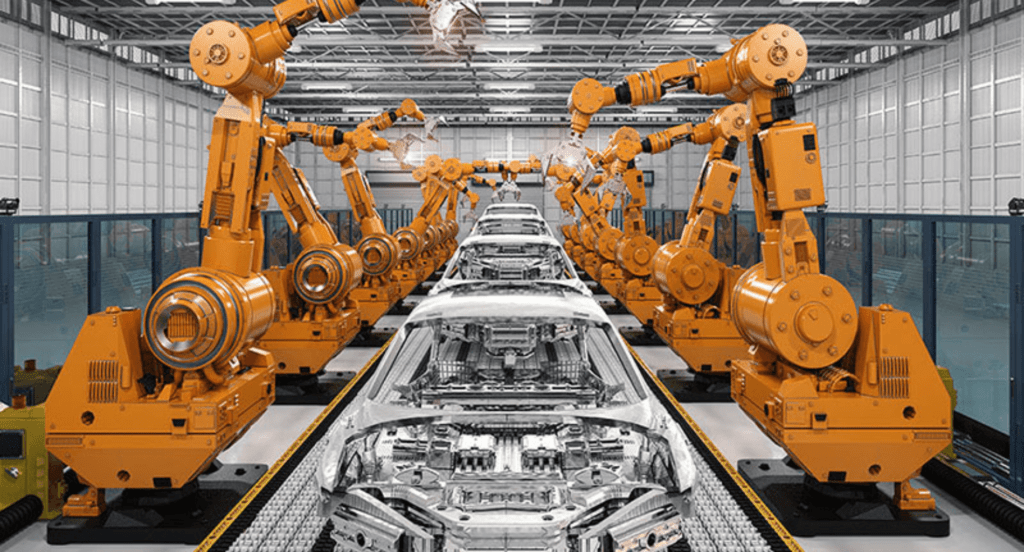
Automotive Industry
Laser cutting and welding is employed in the production of various parts, ranging from complex engine elements to featherweight body panels. Emphasizing the significance of these technologies, Future Market Insights (FMI) projects that from 2022 to 2032, the worldwide market for laser cutting is anticipated to expand at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.8%.
Aerospace and Defense
Laser cutting and welding are ideal for these sectors due to their ability to handle various materials, including high-strength alloys, with extreme precision. The technology is used in fabricating airframe structures, jet engine components, and intricate electronic housings, ensuring these high-performance parts withstand extreme conditions.

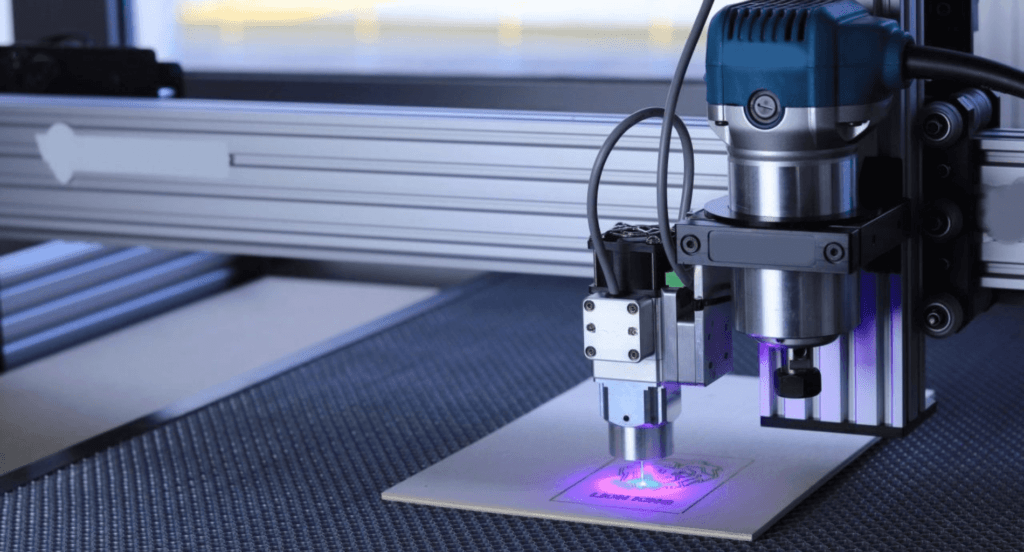
Medical Device Manufacturing
Precision is paramount in medical device manufacturing, where even the smallest error can have significant implications. Laser cutting and welding are widely used for creating surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Their ability to work with delicate, small-scale components makes them indispensable for producing medical devices that are not only precise but also biocompatible and safe for patient use.
5. Cost Analysis and Economic Impact
Laser cutting and welding, while initially demanding a higher investment in machinery and setup, offer long-term cost savings and economic benefits. For instance, the operational efficiency of laser systems can reduce labor costs by up to 30%, according to industry reports. Additionally, the precision of laser technology minimizes material wastage, translating to significant savings in raw material costs.
From an economic perspective, these technologies also contribute to increased productivity. A study indicates that businesses adopting laser cutting and welding can see a productivity increase of 25% on average. This boost in efficiency not only helps businesses scale their operations more effectively but also strengthens their competitive edge in the global market, where speed and quality are key differentiators.

6. Safety and Environmental Considerations
Following the cost analysis, it’s crucial to address the safety and environmental considerations associated with laser cutting and welding. Here are key aspects to consider:
Workplace Safety
Laser cutting and welding require stringent safety measures due to the high-powered lasers and intense heat involved. It’s vital to have proper shielding and protective gear to prevent burns, eye injuries, and exposure to harmful fumes. At Zemetal, ensuring well-ventilated workspaces and using appropriate filtration systems significantly mitigate health risks to operators.

Environmental Impact
While laser technologies are generally cleaner compared to traditional methods, they still pose environmental challenges. The energy consumption of laser equipment, particularly in large-scale operations, is a factor to consider. Moreover, ongoing advancements in laser technology are focusing on increasing energy efficiency, which will further reduce its environmental footprint.
Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with safety and environmental regulations is paramount in laser cutting and welding operations. This includes adhering to standards set by organizations like OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Regular audits and updates to safety protocols ensure that operations not only protect workers but also align with environmental best practices.
7. Challenges and Limitations of Laser Technology
While the safety and environmental considerations of laser cutting and welding are critical, it’s equally important to understand the challenges and limitations of these technologies. Here are some of the key areas where laser technology faces challenges:
Equipment and Maintenance Costs
Despite the long-term cost savings, the initial investment in laser cutting and welding equipment can be significant, posing a barrier for smaller businesses. The maintenance and repair of these high-tech machines require specialized knowledge and can be costly, especially for advanced models like fiber lasers. This aspect of laser technology can impact budgeting and financial planning for companies considering its adoption.
Technical Limitations and Material Constraints
While laser cutting and welding are versatile, they do have limitations in terms of material thickness and type. For instance, laser cutting is less effective with very thick metal plates or materials like reflective metals, which can pose a challenge. Moreover, the quality of cuts and welds can vary depending on the material’s properties, requiring adjustments and sometimes leading to slower processing times or compromised finishes.
Skilled Labor Requirement
Operating laser cutting and welding equipment requires skilled technicians with specialized training. The precision and complexity of these machines necessitate a higher level of expertise compared to traditional metalworking methods. Finding and training qualified personnel can be a challenge, particularly in regions with a limited skilled labor pool, and can also contribute to higher operational costs.
The table below outlines key aspects of operating laser cutting and welding equipment, highlighting the importance of skilled technicians and the challenges associated with finding and training qualified personnel.
| Aspect | Importance | Challenges |
| Specialized Training | Essential for precision and safety | Limited availability of training programs |
| Technician Skill Level | Determines equipment efficiency and product quality | Scarcity of skilled labor in some regions |
| Operational Costs | Influenced by the need for ongoing training | Higher due to training and expertise requirements |
| Equipment Complexity | Requires detailed knowledge for operation and maintenance | Steep learning curve for new technicians |
| Impact on Production | Directly affects output quality and consistency | Delays and increased costs without proper expertise |
8. Future Trends and Developments of Laser Cutting and Welding
As we consider the challenges and limitations of current laser technologies, it’s intriguing to look ahead at future trends and developments. Here are some key areas of future growth:
Enhanced Automation and Smart Systems
The future of laser technology is likely to see an increased focus on enhanced automation and smart system integration. This means more sophisticated control systems that can automate complex tasks, improve precision, and optimize resource use. Such advancements will not only streamline operations but also reduce the need for highly specialized operators, making these technologies more accessible to businesses.
Development of More Compact and Energy-Efficient Lasers
The trend towards developing smaller, more energy-efficient laser systems is set to continue. These advancements aim to make laser equipment more affordable and environmentally friendly, addressing both economic and ecological concerns. Smaller, more efficient lasers will lower the barrier to entry for smaller businesses and contribute to a greener manufacturing process.
Expansion in Non-Metal Applications
Laser cutting and welding are poised to extend beyond traditional metal applications. Research and development are being directed towards adapting these technologies for use with non-metal materials like plastics, composites, and ceramics. This diversification will open up new market opportunities and applications, broadening the reach and versatility of laser cutting and welding in various industrial sectors.
Conclusion
Laser cutting and welding have emerged as game-changers in the world of metal fabrication. As we’ve explored, these technologies are not just about cutting and joining metal; they’re about reinventing how we think about manufacturing processes, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in design and production.
Zemetal, a leader in metal fabrication services, is at the forefront of integrating these advanced techniques into its offerings. To experience the difference that cutting-edge technology can make, contact us today.
Dive Deeper Into Our Resources
Looking for more diverse service options? Browse through our handpicked selections:
Still haven’t found what you’re looking for? Don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re available around the clock to assist you.








